
Have you ever wondered what keeps your vehicle stable and comfortable, even on the bumpiest roads? 🚗 The unsung hero behind this smooth ride is none other than the leaf spring. This simple yet ingenious component has been a cornerstone of vehicle suspension systems for over a century, silently absorbing shocks and maintaining balance.
But what exactly is a leaf spring, and why is it so crucial? 🤔 From classic cars to heavy-duty trucks, leaf springs play a vital role in vehicle performance, load-bearing capacity, and overall driving experience. As we delve into the world of leaf springs, you’ll discover how this seemingly basic technology continues to evolve and adapt to modern automotive needs.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything from the fundamental workings of leaf springs to cutting-edge innovations in the field. We’ll uncover the various applications across different vehicles, discuss materials and manufacturing processes, and even share tips on maintenance and care. So, buckle up as we spring into action and unravel the fascinating world of leaf springs! 🍃🔧
Understanding Leaf Springs
A. Definition and basic structure
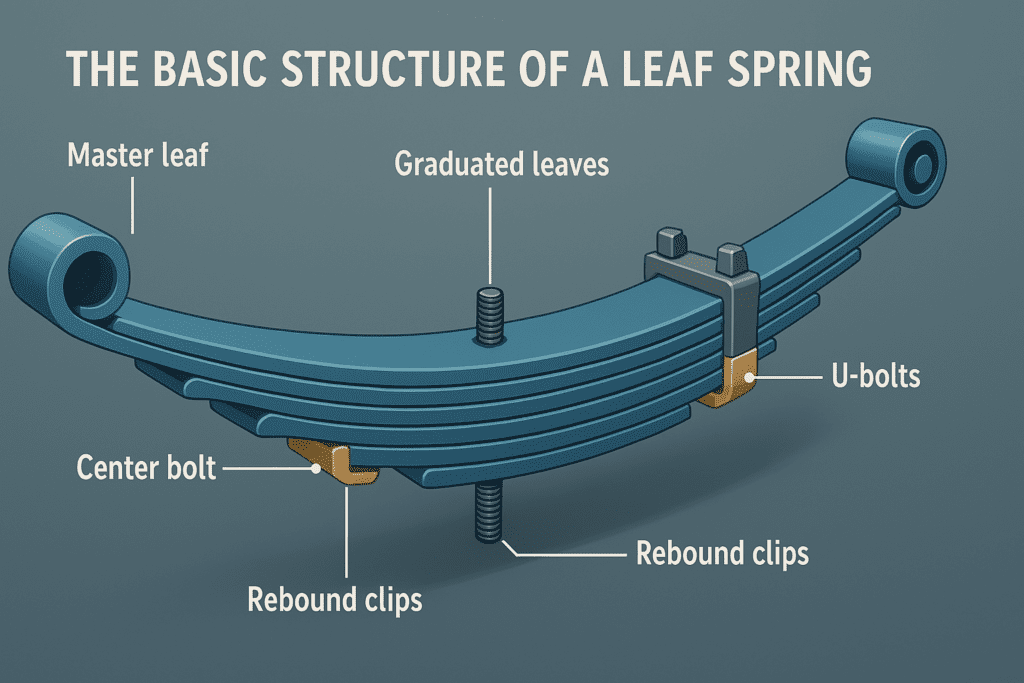
Leaf springs are a fundamental component of vehicle suspension systems, designed to absorb shock and provide a smooth ride. These simple yet effective mechanical devices consist of several layers of curved metal strips, called leaves, stacked on top of each other. The leaves are typically made of high-strength steel and are held together by a center bolt and two U-bolts at the ends.
The basic structure of a leaf spring includes:
- Master leaf: The longest and topmost leaf
- Graduated leaves: Progressively shorter leaves beneath the master leaf
- Center bolt: Holds the leaves together at the middle
- U-bolts: Secure the spring to the axle
- Rebound clips: Prevent leaf separation during suspension movement
Here’s a simplified representation of a leaf spring’s structure:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Master leaf | Longest leaf, forms the main arch |
| Graduated leaves | Shorter leaves, provide additional support |
| Center bolt | Holds leaves together at the center |
| U-bolts | Attach the spring assembly to the vehicle axle |
| Rebound clips | Prevent leaf separation during rebound |
B. Historical development
The concept of leaf springs dates back to medieval times, with early forms used in horse-drawn carriages. However, their application in automotive suspension systems began in the late 19th century. The historical development of leaf springs can be outlined as follows:
- Ancient origins: Primitive leaf springs made from wood in chariots and carriages
- Industrial Revolution: Transition to metal leaf springs for improved durability
- Early automobiles: Adoption of leaf springs in the first motor vehicles
- Mid-20th century: Widespread use in cars, trucks, and commercial vehicles
- Modern era: Continued use in heavy-duty vehicles and some SUVs
C. Types of leaf springs
Leaf springs come in various configurations to suit different vehicle types and suspension requirements. The main types of leaf springs include:
- Multi-leaf springs: The most common type, consisting of several leaves of varying lengths stacked together. These provide a balance of strength and flexibility.
- Mono-leaf springs: A single, tapered leaf that offers reduced weight and friction compared to multi-leaf springs. These are often used in lighter vehicles or performance applications.
- Parabolic leaf springs: Feature fewer leaves with a parabolic taper, providing better ride quality and reduced weight compared to conventional multi-leaf springs.
- Helper springs: Additional leaf springs that engage only under heavy loads, providing extra support when needed.
- Transverse leaf springs: Mounted perpendicular to the vehicle’s length, often used in some sports cars and racing vehicles for improved handling.
Each type of leaf spring offers unique characteristics:
| Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Multi-leaf | High load capacity, durability | Heavier, more friction |
| Mono-leaf | Lightweight, reduced friction | Lower load capacity |
| Parabolic | Better ride quality, lighter weight | More expensive to manufacture |
| Helper | Adjustable load support | Added complexity |
| Transverse | Improved handling, compact design | Limited to specific applications |
Understanding these different types of leaf springs is crucial for selecting the appropriate suspension system for various vehicles and applications. As we move forward, we’ll explore how these versatile components function to provide a comfortable and stable ride.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
How Leaf Springs Work

Principles of operation
Leaf springs operate on the fundamental principle of elastic deformation. When a load is applied, the spring flexes and absorbs energy, then returns to its original shape when the load is removed. This simple yet effective mechanism allows leaf springs to provide both support and cushioning for vehicles.
The leaf spring consists of several layers of curved metal strips, called leaves, stacked on top of each other. The longest leaf, known as the master leaf, spans the entire length of the spring and is typically attached to the vehicle’s frame at both ends. Shorter leaves are progressively stacked beneath it, creating a tapered profile that distributes stress more evenly.
Load distribution
One of the key strengths of leaf springs is their ability to effectively distribute loads across the vehicle’s frame. This is achieved through the following mechanisms:
- Multi-leaf design: The layered structure allows for graduated load bearing
- Variable thickness: Leaves can be manufactured with different thicknesses to optimize load distribution
- Progressive rate: As the load increases, more leaves engage, providing a non-linear response
| Load Level | Engaged Leaves | Spring Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Light | 1-2 | Soft |
| Medium | 3-4 | Moderate |
| Heavy | All | Firm |
This progressive engagement ensures that the suspension remains comfortable under light loads while still providing adequate support for heavier loads.
Suspension dynamics
Leaf springs play a crucial role in a vehicle’s suspension dynamics, influencing factors such as:
- Ride comfort
- Handling characteristics
- Vehicle stability
- Load carrying capacity
The interleaf friction in leaf springs provides natural damping, which helps to absorb road shocks and vibrations. This damping effect is particularly beneficial for heavy-duty vehicles, as it reduces the need for additional shock absorbers.
Advantages over other suspension systems
Leaf springs offer several advantages compared to other suspension systems:
- Simplicity: Fewer components lead to easier maintenance and lower production costs
- Durability: Robust design withstands harsh conditions and heavy loads
- Space efficiency: Compact profile allows for more cargo space in trucks and utility vehicles
- Load capacity: Excellent for supporting heavy loads in commercial vehicles
- Axle location: Leaf springs can serve as both a spring and a locating device for the axle
While coil springs and air suspensions have gained popularity in passenger vehicles, leaf springs remain the preferred choice for many commercial and off-road applications due to their unique combination of strength, simplicity, and load-bearing capabilities.
Now that we’ve explored how leaf springs work, let’s examine their various applications across different industries and vehicle types.
Applications of Leaf Springs

A. Automotive industry
Leaf springs have been a staple in the automotive industry for decades, particularly in trucks and larger vehicles. Their simple yet effective design provides excellent load-bearing capacity and helps absorb road shocks, making them ideal for various applications.
- Light-duty trucks
- SUVs
- Vans
- Classic cars
In the automotive sector, leaf springs offer several advantages:
- Cost-effective suspension solution
- Durability and longevity
- Excellent load-carrying capacity
- Simplified maintenance
B. Heavy-duty vehicles
The robust nature of leaf springs makes them particularly suitable for heavy-duty vehicles that require superior load-bearing capabilities and stability.
| Vehicle Type | Leaf Spring Benefits |
|---|---|
| Semi-trucks | Enhanced load distribution |
| Dump trucks | Improved stability during unloading |
| Buses | Smoother ride for passengers |
| Fire trucks | Better weight management for equipment |
C. Railway systems
In the railway industry, leaf springs play a crucial role in ensuring smooth and safe operations. They are commonly used in:
- Freight cars
- Passenger coaches
- Locomotive suspensions
Leaf springs in railway systems help:
- Absorb vibrations and shocks from track irregularities
- Distribute weight evenly across wheels
- Enhance overall ride comfort for passengers
D. Industrial machinery
The versatility of leaf springs extends to various industrial applications, where they are utilized in:
- Conveyor systems
- Crushing equipment
- Vibrating screens
- Heavy-duty presses
In these applications, leaf springs provide:
- Shock absorption to protect sensitive components
- Consistent performance under high-stress conditions
- Reduced maintenance requirements
E. Agricultural equipment
The agricultural sector also benefits significantly from the use of leaf springs in various types of machinery and equipment.
- Tractors
- Harvesters
- Plows
- Trailers
Leaf springs in agricultural equipment offer:
- Improved traction on uneven terrain
- Better load distribution for heavy implements
- Enhanced stability during field operations
- Increased durability in harsh working conditions
The wide-ranging applications of leaf springs across these diverse industries underscore their importance and versatility. As we move forward, we’ll explore the materials used in leaf spring manufacturing and the processes involved in creating these essential components.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Leaf Spring Materials and Manufacturing

Common materials used
Leaf springs are primarily constructed using a variety of high-strength materials, each chosen for its specific properties and suitability for different applications. The most commonly used materials include:
- Steel Alloys:
- SAE 5160
- SAE 9260
- 50CrV4
- 55Si7
- Composite Materials:
- Glass Fiber Reinforced Plastic (GFRP)
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Plastic (CFRP)
Here’s a comparison table of the most common materials used in leaf spring manufacturing:
| Material | Strength | Weight | Corrosion Resistance | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAE 5160 | High | Heavy | Moderate | Low |
| SAE 9260 | Very High | Heavy | Moderate | Moderate |
| 50CrV4 | High | Heavy | Good | Moderate |
| 55Si7 | Very High | Heavy | Good | High |
| GFRP | High | Light | Excellent | High |
| CFRP | Very High | Very Light | Excellent | Very High |
Manufacturing processes
The manufacturing process of leaf springs involves several stages, each crucial for ensuring the spring’s performance and durability. The main steps include:
- Material Selection: Choosing the appropriate material based on the application requirements.
- Cutting: The selected material is cut to the required length and width.
- Heating: The cut material is heated to high temperatures (typically around 800-900°C) to make it malleable.
- Forming: The heated material is shaped into the desired leaf spring profile using hydraulic presses or roller forming machines.
- Eye Rolling: For springs requiring eyes at the ends, the material is rolled to form these features.
- Quenching: The formed spring is rapidly cooled to increase hardness and strength.
- Tempering: The quenched spring is reheated to a lower temperature to relieve internal stresses and improve toughness.
- Shot Peening: The spring surface is bombarded with small metal balls to induce compressive stress, enhancing fatigue resistance.
- Assembly: For multi-leaf springs, individual leaves are stacked and secured together.
Heat treatment and finishing
Heat treatment is a critical process in leaf spring manufacturing, significantly influencing the spring’s mechanical properties. The main heat treatment processes include:
- Quenching: Rapidly cooling the heated spring in oil or water to increase hardness and strength.
- Tempering: Reheating the quenched spring to a lower temperature (typically 400-500°C) to relieve internal stresses and improve toughness.
- Stress Relieving: A low-temperature heat treatment to reduce residual stresses from manufacturing.
After heat treatment, several finishing processes are applied to enhance the leaf spring’s performance and appearance:
- Shot Peening: Improves fatigue resistance by inducing compressive stress on the surface.
- Painting or Coating: Protects against corrosion and improves aesthetics.
- Graphite Coating: Applied between leaves to reduce friction and noise.
- Edge Trimming: Removes any sharp edges to prevent injury during handling.
These manufacturing and finishing processes ensure that leaf springs meet the required specifications for strength, durability, and performance in their intended applications. The choice of material and manufacturing process depends on factors such as the vehicle type, load capacity, and operating conditions.
Maintenance and Care of Leaf Springs

Regular inspection tips
To ensure the longevity and optimal performance of leaf springs, regular inspections are crucial. Here are some essential tips for conducting thorough checks:
- Visual examination: Look for signs of wear, cracks, or rust on the leaf spring components.
- Check for sagging: Measure the vehicle’s ride height to detect any significant changes.
- Inspect U-bolts: Ensure they are tight and not corroded.
- Examine bushings: Look for signs of deterioration or excessive play.
- Check for misalignment: Verify that the leaves are properly aligned and not shifted.
Implementing a routine inspection schedule can help catch issues early and prevent costly repairs. Here’s a suggested timeline for leaf spring inspections:
| Frequency | Inspection Type |
|---|---|
| Monthly | Quick visual check |
| Quarterly | Thorough examination |
| Annually | Professional inspection |
Lubrication requirements
Proper lubrication is essential for maintaining the smooth operation of leaf springs and preventing premature wear. Here are key points to remember:
- Frequency: Lubricate leaf springs every 3,000 to 5,000 miles or as recommended by the vehicle manufacturer.
- Lubricant type: Use a high-quality, water-resistant grease specifically designed for leaf springs.
- Application method: Apply lubricant between the leaves using a grease gun or spray lubricant.
- Focus areas: Pay special attention to the ends of the leaves and the center bolt area.
- Clean before lubricating: Remove dirt and debris before applying new lubricant.
It’s important to note that some modern leaf springs come with plastic inserts or are made of composite materials that don’t require lubrication. Always consult your vehicle’s manual for specific recommendations.
Replacement indicators
Knowing when to replace leaf springs is crucial for maintaining vehicle safety and performance. Here are key indicators that suggest it’s time for a replacement:
- Visible cracks or breaks: Any visible damage to the leaves is a clear sign of needed replacement.
- Excessive sagging: If your vehicle sits noticeably lower than usual, it may be time for new springs.
- Uneven tire wear: Worn leaf springs can cause uneven weight distribution, leading to irregular tire wear.
- Reduced ride quality: If you notice increased bouncing or a rougher ride, your leaf springs may be worn out.
- Age: Even without visible wear, leaf springs should be replaced every 100,000 to 150,000 miles as a precautionary measure.
When replacing leaf springs, it’s often recommended to replace them in pairs to ensure balanced suspension performance. Always use high-quality replacement parts that match your vehicle’s specifications.
Regular maintenance and timely replacements of leaf springs not only ensure a smoother ride but also contribute to the overall safety and longevity of your vehicle. By following these guidelines for inspection, lubrication, and replacement, you can maximize the performance and lifespan of your leaf springs. In the next section, we’ll explore recent innovations in leaf spring technology that are shaping the future of vehicle suspension systems.
Innovations in Leaf Spring Technology

Composite Materials
Leaf spring technology has taken a significant leap forward with the introduction of composite materials. These innovative materials, typically consisting of fiberglass-reinforced plastics or carbon fiber composites, offer several advantages over traditional steel leaf springs:
- Reduced weight (up to 70% lighter than steel)
- Improved corrosion resistance
- Enhanced fatigue life
- Better noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) characteristics
| Property | Steel Leaf Springs | Composite Leaf Springs |
|---|---|---|
| Weight | Heavy | Lightweight |
| Corrosion Resistance | Low | High |
| Fatigue Life | Moderate | Extended |
| NVH Performance | Good | Excellent |
The adoption of composite leaf springs has been particularly beneficial in the automotive and commercial vehicle sectors, where weight reduction directly translates to improved fuel efficiency and increased payload capacity.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Lightweight Designs
Innovative lightweight designs have revolutionized leaf spring technology. Engineers have developed new configurations that maintain or even improve performance while significantly reducing weight:
- Multi-leaf to mono-leaf conversion
- Tapered leaf designs
- Variable thickness springs
- Parabolic leaf springs
These designs not only reduce vehicle weight but also contribute to better ride quality and handling characteristics. For instance, parabolic leaf springs offer a more progressive spring rate, providing a smoother ride under various load conditions.
Integration with Air Suspension Systems
A groundbreaking innovation in leaf spring technology is its integration with air suspension systems. This hybrid approach combines the best of both worlds:
- Leaf springs provide primary load support and lateral stability
- Air springs offer adjustable ride height and improved comfort
Benefits of this integration include:
- Enhanced load-carrying capacity
- Improved ride quality across different road conditions
- Adjustable vehicle height for various applications
- Better weight distribution and handling
This technology has found widespread application in commercial trucks, buses, and high-end recreational vehicles, offering a versatile suspension solution for diverse operational requirements.
Smart Leaf Springs with Sensors
The latest frontier in leaf spring innovation is the development of smart leaf springs equipped with sensors. These advanced systems incorporate:
- Strain gauges
- Piezoelectric sensors
- Fiber optic sensors
Smart leaf springs provide real-time data on:
- Load distribution
- Stress levels
- Spring deflection
- Temperature
This information enables:
- Predictive maintenance
- Real-time load monitoring
- Enhanced vehicle stability control
- Improved overall vehicle performance and safety
As we continue to push the boundaries of leaf spring technology, these innovations are reshaping the automotive and transportation industries, offering improved efficiency, safety, and performance across a wide range of vehicles and applications.
10 FAQs

1. What is a leaf spring?
A leaf spring is a simple form of spring commonly used for the suspension in wheeled vehicles. It consists of several layers of metal strips (leaves) of varying lengths, stacked on top of each other to form a multi-leaf spring assembly.
2. What are the main advantages of leaf springs?
Leaf springs offer several advantages:
- Simplicity in design
- Cost-effectiveness
- Durability
- Load-bearing capacity
- Ability to distribute weight evenly
3. In which vehicles are leaf springs commonly used?
Leaf springs are frequently used in:
- Heavy-duty trucks
- SUVs
- Vans
- Railway carriages
- Some classic cars
4. How long do leaf springs typically last?
The lifespan of leaf springs can vary depending on usage and maintenance. Here’s a general guideline:
| Vehicle Type | Average Lifespan |
|---|---|
| Passenger cars | 100,000 – 150,000 miles |
| Light trucks | 100,000 – 200,000 miles |
| Heavy-duty trucks | 200,000 – 300,000 miles |
5. What are the signs that leaf springs need replacement?
Common indicators include:
- Vehicle sagging on one side
- Uneven tire wear
- Squeaking or creaking noises
- Decreased ride comfort
- Visible cracks or breaks in the spring
6. Can leaf springs be repaired?
In some cases, leaf springs can be repaired by replacing individual leaves or re-arching the spring. However, for safety reasons, it’s often recommended to replace the entire spring assembly.
7. What materials are used to make leaf springs?
Leaf springs are typically made from:
- High-carbon steel
- Alloy steel
- Stainless steel
- Composite materials (in modern applications)
8. How do leaf springs compare to coil springs?
| Aspect | Leaf Springs | Coil Springs |
|---|---|---|
| Load capacity | Higher | Lower |
| Space efficiency | Less compact | More compact |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Ride comfort | Generally firmer | Generally softer |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
9. Are there different types of leaf springs?
Yes, there are several types:
- Multi-leaf springs
- Mono-leaf springs
- Parabolic leaf springs
- Semi-elliptical leaf springs
- Quarter-elliptical leaf springs
10. How often should leaf springs be maintained?
Regular maintenance of leaf springs should include:
- Visual inspection every 6 months
- Lubrication every 12 months or 12,000 miles
- Tightening of U-bolts and center bolts annually
Regular maintenance can significantly extend the life of your leaf springs and ensure optimal vehicle performance.

Leaf springs have proven to be a crucial component in vehicle suspension systems, offering reliability, durability, and cost-effectiveness. From their basic structure to their diverse applications in automotive, agricultural, and industrial sectors, these simple yet effective devices continue to play a vital role in modern engineering. The evolution of materials and manufacturing processes has further enhanced their performance and longevity, making them a preferred choice for many vehicle manufacturers.
As technology advances, innovations in leaf spring design and materials promise even greater improvements in ride quality, weight reduction, and overall vehicle performance. Whether you’re a car enthusiast, a mechanic, or simply curious about automotive engineering, understanding leaf springs can provide valuable insights into the complexities of vehicle suspension systems. By properly maintaining and caring for leaf springs, vehicle owners can ensure optimal performance and extend the lifespan of their suspension components.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone

