Imagine cruising down a rain-slicked highway when suddenly, a car cuts you off. Your heart races as you slam on the brakes, but instead of skidding out of control, your vehicle comes to a smooth, controlled stop. This life-saving moment is all thanks to a revolutionary technology: the Anti-lock Braking System (ABS).
ABS has become a standard safety feature in modern vehicles, but do you really know how it works? From its humble beginnings to its current sophisticated state, ABS has evolved to become an indispensable part of automotive safety. In this blog post, we’ll dive deep into the world of ABS, exploring its mechanics, benefits, and how it performs in various driving conditions. We’ll also look at the technology’s evolution and provide tips on maintaining your vehicle’s ABS for optimal performance.
So, fasten your seatbelts as we take you on a journey through the ins and outs of Anti-lock Braking Systems. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or simply curious about the technology that keeps you safe on the road, this guide will give you a comprehensive understanding of ABS and why it’s a crucial component in modern vehicles.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
1. Understanding ABS Technology
1.1. Definition and basic principles
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) is a crucial safety feature in modern vehicles designed to prevent wheel lock-up during sudden or hard braking. The basic principle behind ABS is to maintain traction between the tires and the road surface, allowing the driver to maintain steering control while braking.
ABS works by rapidly modulating brake pressure, typically 15-20 times per second, to prevent the wheels from locking up. This pulsing action allows the wheels to continue rotating, even during emergency braking situations, which helps maintain steering control and reduces stopping distances on most surfaces.
1.2. Components of an ABS system

An ABS system consists of several key components working together to ensure optimal braking performance:
- Wheel speed sensors
- Hydraulic control unit
- ABS control module
- Brake lines and valves
- ABS warning light
Let’s take a closer look at each component:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Wheel speed sensors | Monitor the rotation speed of each wheel |
| Hydraulic control unit | Regulates brake fluid pressure to each wheel |
| ABS control module | Processes sensor data and controls the hydraulic unit |
| Brake lines and valves | Distribute brake fluid and control pressure to each wheel |
| ABS warning light | Alerts the driver to potential system malfunctions |
The wheel speed sensors continuously monitor the rotation speed of each wheel, sending this information to the ABS control module. When the control module detects that one or more wheels are about to lock up, it signals the hydraulic control unit to rapidly adjust brake fluid pressure to the affected wheel(s).
1.3. How ABS improves vehicle safety
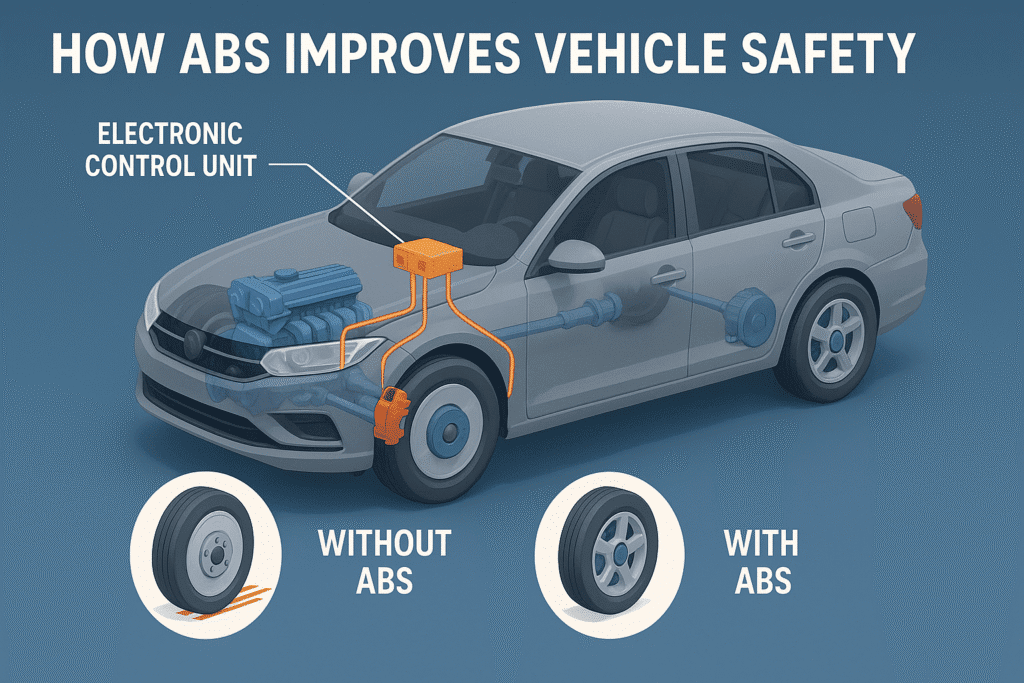
ABS technology significantly enhances vehicle safety in several ways:
- Prevents wheel lock-up: By maintaining wheel rotation during braking, ABS helps prevent skidding and loss of control.
- Maintains steering control: With the wheels still rotating, drivers can steer around obstacles even while braking hard.
- Reduces stopping distances: On most surfaces, particularly wet or slippery roads, ABS can help reduce the vehicle’s stopping distance.
- Improves stability: By preventing wheel lock-up, ABS helps maintain the vehicle’s stability during emergency braking situations.
- Enhances driver confidence: Knowing that the vehicle is equipped with ABS can give drivers more confidence in challenging driving conditions.
These safety improvements have made ABS a standard feature in most modern vehicles, significantly reducing the number of accidents caused by loss of control during braking. As we move forward, we’ll explore the mechanics behind how ABS achieves these safety benefits, providing a deeper understanding of this crucial automotive technology.
2. The Mechanics Behind ABS
2.1. Wheel speed sensors

At the heart of the ABS system are wheel speed sensors, crucial components that monitor the rotational speed of each wheel. These sensors are typically mounted on the wheel hub or axle and use electromagnetic principles to generate signals. As the wheel rotates, the sensor detects changes in the magnetic field, producing a pulse signal that’s proportional to the wheel’s speed.
- Types of wheel speed sensors:
- Variable reluctance sensors (older technology)
- Hall effect sensors (modern, more accurate)
The data from these sensors is continuously sent to the Electronic Control Unit (ECU), allowing for real-time monitoring of wheel speeds.
2.2. Hydraulic valves

Hydraulic valves play a pivotal role in controlling brake fluid pressure to each wheel. These valves can rapidly open and close, modulating the brake pressure as needed. There are typically three positions for each valve:
- Open: Allows pressure from the master cylinder to the brake
- Closed: Isolates brake from master cylinder
- Release: Allows pressure to be released from the brake
| Valve Position | Function | Effect on Braking |
|---|---|---|
| Open | Normal braking | Full brake pressure applied |
| Closed | Pressure hold | Maintains current brake pressure |
| Release | Pressure reduction | Decreases brake pressure |
The precise control of these valves enables the ABS to prevent wheel lock-up during hard braking or on slippery surfaces.
2.3. Electronic control unit (ECU)

The ECU is the brain of the ABS system, processing data from the wheel speed sensors and controlling the hydraulic valves. This sophisticated computer analyzes wheel speed information many times per second, detecting when a wheel is about to lock up. When impending lock-up is detected, the ECU rapidly commands the hydraulic valves to modulate brake pressure.
Key functions of the ECU include:
- Continuous monitoring of wheel speeds
- Comparison of wheel speeds to vehicle speed
- Detection of wheel deceleration rates
- Activation of the hydraulic pump when necessary
2.4. Hydraulic pump

The hydraulic pump is activated by the ECU when it’s necessary to increase brake pressure after it has been reduced. During ABS activation, the pump quickly restores pressure to the braking system, ensuring that braking force is maintained even as the system rapidly modulates brake pressure to prevent wheel lock-up.
Now that we’ve explored the core components of the ABS system, let’s examine how these elements work together to provide the numerous benefits of anti-lock braking systems in various driving conditions.
3. Benefits of Anti-lock Braking Systems
3.1. Preventing wheel lock-up
One of the primary benefits of Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) is its ability to prevent wheel lock-up during sudden or hard braking. When a driver applies excessive force to the brake pedal, conventional braking systems can cause the wheels to stop rotating completely, leading to skidding and loss of control. ABS, however, uses advanced sensors and hydraulic valves to rapidly pulse the brakes, allowing the wheels to maintain rotation while still providing maximum braking force.
This pulsing action, which can occur up to 15 times per second, ensures that the wheels continue to rotate even under extreme braking conditions. By preventing wheel lock-up, ABS significantly reduces the risk of skidding and allows the driver to maintain better control of the vehicle during emergency stops.
3.2. Maintaining steering control during braking
Another crucial advantage of ABS is its ability to help drivers maintain steering control while braking. When wheels lock up, the vehicle loses its ability to respond to steering input, potentially leading to dangerous situations. ABS prevents this by keeping the wheels rotating, allowing the tires to maintain traction with the road surface.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
This continuous rotation enables drivers to steer around obstacles or adjust their trajectory while applying the brakes, a feature particularly valuable in emergency situations. The table below illustrates the difference in steering control between vehicles with and without ABS:
| Scenario | Vehicle without ABS | Vehicle with ABS |
|---|---|---|
| Emergency braking | Limited steering control | Maintained steering control |
| Obstacle avoidance | Difficult to maneuver | Ability to steer around obstacles |
| Cornering while braking | High risk of skidding | Improved stability and control |
3.3. Reduced stopping distances on slippery surfaces

ABS truly shines when it comes to reducing stopping distances on slippery surfaces such as wet roads, snow, or ice. By preventing wheel lock-up and maintaining optimal traction, ABS allows the vehicle to come to a stop more quickly and safely in challenging conditions.
On slippery surfaces, locked wheels tend to slide, increasing the stopping distance. ABS, however, continuously adjusts brake pressure to find the optimal balance between braking force and wheel rotation, resulting in shorter stopping distances. This advantage is particularly notable in the following situations:
- Wet roads
- Snowy or icy conditions
- Gravel or loose surfaces
- Oil-covered patches
3.4. Increased overall vehicle stability
Finally, ABS contributes significantly to overall vehicle stability during braking maneuvers. By preventing wheel lock-up and maintaining steering control, ABS helps keep the vehicle balanced and stable, reducing the risk of spinning or sliding out of control.
This increased stability is especially beneficial in the following scenarios:
- Cornering at high speeds
- Sudden lane changes
- Evasive maneuvers
- Braking on uneven surfaces
Moreover, ABS works in conjunction with other safety systems like Electronic Stability Control (ESC) and Traction Control Systems (TCS) to provide a comprehensive safety package. This integration further enhances the vehicle’s stability and handling characteristics, making driving safer and more controlled in various conditions.
With these significant benefits, it’s clear why ABS has become a standard safety feature in modern vehicles. As we explore ABS in different driving conditions, we’ll see how these advantages translate into real-world scenarios, further highlighting the importance of this crucial safety technology.
4. ABS in Different Driving Conditions
4.1. Performance on dry roads

ABS technology shines on dry roads, offering drivers enhanced control and safety during emergency braking situations. On dry surfaces, ABS prevents wheel lock-up, allowing the driver to maintain steering control while braking hard. This is particularly crucial when navigating sudden obstacles or during evasive maneuvers.
| Aspect | Without ABS | With ABS |
|---|---|---|
| Stopping distance | Potentially longer | Optimized |
| Steering control | Limited or lost | Maintained |
| Tire wear | Uneven and excessive | Reduced |
| Vehicle stability | Compromised | Enhanced |
4.2. Effectiveness in wet weather

Wet roads present unique challenges, but ABS proves its worth in these conditions. The system’s ability to prevent wheel lock-up is even more critical on slippery surfaces, where the risk of hydroplaning is higher.
Benefits of ABS in wet conditions:
- Reduced stopping distances
- Improved directional stability
- Enhanced traction during cornering
- Minimized risk of skidding
4.3. ABS and snow or ice
Winter driving conditions are where ABS truly demonstrates its versatility. While the system’s effectiveness can vary depending on the specific snow or ice conditions, it generally provides significant advantages:
- Prevents wheel lock-up on icy surfaces
- Maintains steering control in snowy conditions
- Helps navigate slush-covered roads more safely
- Reduces the risk of sliding during sudden stops
It’s important to note that in deep snow, ABS may slightly increase stopping distances. This is because a small amount of wheel lock-up can help build up snow in front of the tires, creating a natural stopping wedge. However, the trade-off of maintaining steering control is generally considered more beneficial.
4.4. Off-road capabilities

While ABS is primarily designed for on-road use, many modern systems are adapted for off-road driving. Off-road ABS often functions differently from its on-road counterpart to accommodate the unique challenges of unpaved surfaces.
Off-road ABS features:
- Allows for more wheel slip to dig into loose surfaces
- Adapts to varying terrain types (sand, gravel, mud)
- Often includes a separate off-road mode that can be activated by the driver
When driving off-road, ABS helps maintain vehicle control on loose or uneven surfaces, reducing the risk of sliding or rolling. However, experienced off-road drivers may prefer to disable ABS in certain situations where controlled wheel lock-up can be advantageous.
Now that we’ve explored how ABS performs in various driving conditions, let’s delve into the evolution of this crucial safety technology and how it has improved over the years.
5. Evolution of ABS Technology
5.1. Early mechanical systems
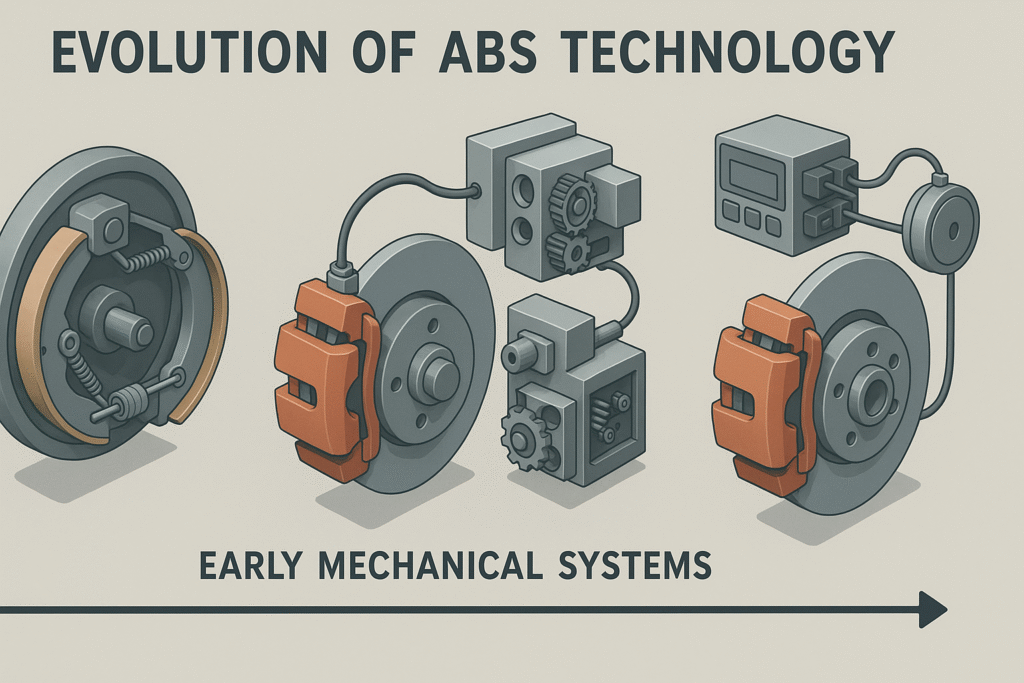
The evolution of Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS) began with early mechanical systems that laid the foundation for modern electronic ABS. These pioneering systems, developed in the mid-20th century, aimed to prevent wheel lock-up during braking, especially on slippery surfaces.
One of the earliest examples was the Maxaret system, introduced in the 1950s for aircraft use. This mechanical system used a flywheel to detect wheel deceleration and modulate brake pressure accordingly. While effective for its time, the Maxaret system was bulky and limited in its application to road vehicles.
| System | Year | Application | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maxaret | 1950s | Aircraft | Flywheel-based, mechanical |
| Jensen FF | 1966 | Road vehicles | Dunlop Maxaret system adapted for cars |
| Chrysler Sure-Brake | 1971 | Road vehicles | Four-wheel system, limited production |
5.2. Introduction of electronic ABS

The real breakthrough in ABS technology came with the introduction of electronic systems in the 1970s. These systems utilized sensors, control units, and valves to monitor wheel speed and modulate brake pressure with greater precision and speed than their mechanical predecessors.
Bosch played a pivotal role in this development, introducing the first production electronic ABS in 1978. This system was initially featured in high-end vehicles like the Mercedes-Benz S-Class and BMW 7 Series. The electronic ABS quickly proved its worth, significantly improving vehicle safety and handling during emergency braking situations.
Key advancements in electronic ABS included:
- Faster response times
- More accurate wheel speed sensing
- Improved modularity and integration with vehicle systems
- Reduced system weight and complexity
5.3. Integration with other safety features

As ABS technology matured, it became the cornerstone for integrating various other vehicle safety systems. This integration led to the development of comprehensive vehicle stability control systems, enhancing overall safety and performance.
Some key integrations include:
- Electronic Stability Control (ESC)
- Traction Control Systems (TCS)
- Emergency Brake Assist (EBA)
- Electronic Brake-force Distribution (EBD)
These integrated systems work in harmony to provide a holistic approach to vehicle safety, utilizing the ABS infrastructure as a foundation for more advanced functionalities.
5.4. Future developments in ABS technology

The future of ABS technology is closely tied to the advancement of autonomous vehicles and connected car systems. As vehicles become more intelligent and interconnected, ABS systems are evolving to meet new challenges and opportunities.
Some promising developments include:
- Predictive ABS: Using data from vehicle sensors, GPS, and even other vehicles to anticipate braking needs
- AI-enhanced ABS: Employing machine learning algorithms to optimize braking performance based on driver behavior and road conditions
- Integration with regenerative braking in electric vehicles
- Enhanced compatibility with advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
As we look towards the future of automotive safety, it’s clear that ABS will continue to play a crucial role. The next generation of ABS technology promises to offer even greater levels of safety, efficiency, and integration with other vehicle systems, paving the way for safer and more intelligent vehicles on our roads.
6. Maintaining Your Vehicle’s ABS
6.1. Regular inspections
Regular inspections are crucial for maintaining your vehicle’s Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) in optimal condition. These checks help identify potential issues before they escalate into more serious problems. Here’s a list of key inspection points:
- ABS warning light
- Brake fluid level and quality
- Wheel speed sensors
- ABS module
- Brake pads and rotors
To ensure a thorough inspection, follow this simple maintenance schedule:
| Frequency | Inspection Task |
|---|---|
| Monthly | Check ABS warning light and brake fluid level |
| Quarterly | Inspect brake pads and rotors |
| Annually | Full ABS system diagnostic check |
6.2. Common ABS issues and warning signs
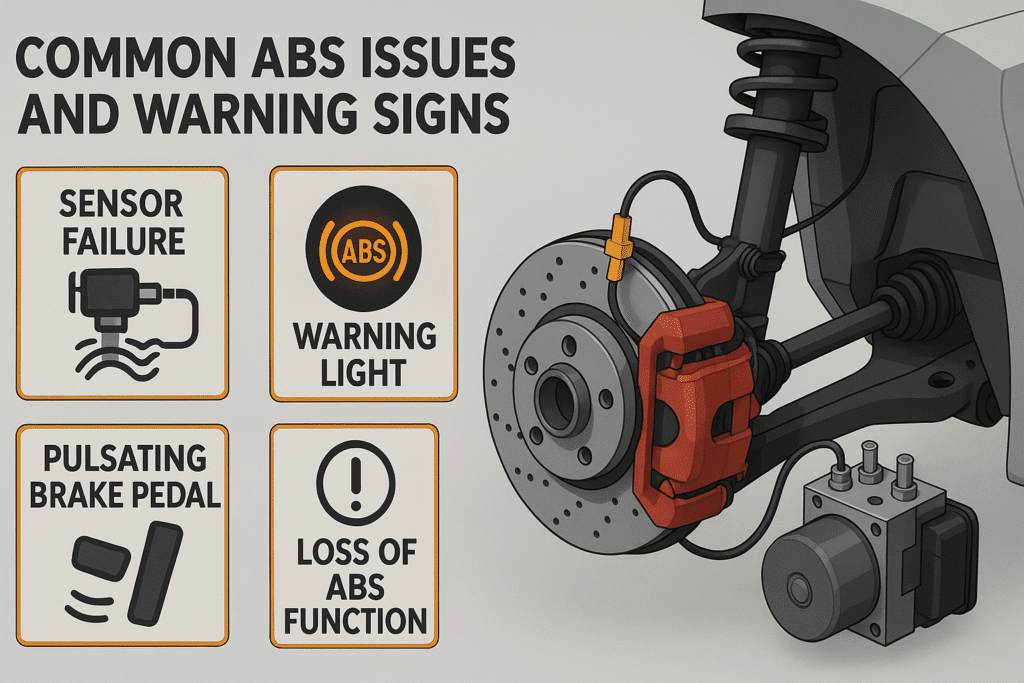
Being aware of common ABS issues and their warning signs can help you address problems promptly. Here are some indicators that your ABS might need attention:
- Illuminated ABS warning light
- Pulsating brake pedal during normal braking
- Increased stopping distance
- Unusual noises when braking
- Brake pedal becoming hard to press
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s essential to have your vehicle inspected by a qualified technician as soon as possible.
6.3. Professional servicing requirements
While some aspects of ABS maintenance can be performed at home, certain tasks require professional attention. Professional servicing typically includes:
- Comprehensive system diagnostics
- Brake fluid replacement
- ABS module testing and repair
- Wheel speed sensor calibration
- Software updates for the ABS control unit
It’s recommended to have your ABS professionally serviced according to your vehicle manufacturer’s guidelines, usually every 2-3 years or 30,000-50,000 miles, whichever comes first.
6.4. DIY maintenance tips
Although professional servicing is crucial, there are several DIY maintenance tasks you can perform to keep your ABS in good condition:
- Regularly check brake fluid levels and top up if necessary
- Inspect brake pads and rotors for wear
- Keep wheel speed sensors clean from debris
- Pay attention to any changes in braking performance
- Address any illuminated warning lights promptly
| DIY Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Check brake fluid | Monthly |
| Inspect brake pads | Quarterly |
| Clean wheel speed sensors | Bi-annually |
By following these maintenance practices, you can help ensure your ABS remains in optimal condition, providing reliable performance when you need it most. Regular care not only extends the life of your ABS but also contributes to your overall safety on the road. In the next section, we’ll summarize the key points discussed throughout this guide and provide some final thoughts on the importance of ABS in modern vehicles.
7. Conclusion
7.1. Key Takeaways
As we wrap up our exploration of Anti-lock Braking Systems (ABS), let’s recap the essential points:
- ABS is a crucial safety feature that prevents wheel lock-up during sudden braking
- The system works by rapidly pulsing the brakes, allowing the driver to maintain steering control
- ABS offers significant benefits in various driving conditions, especially on wet or slippery roads
- Regular maintenance is vital to ensure optimal ABS performance
7.2. Future of ABS Technology
Looking ahead, ABS technology continues to evolve:
- Integration with other advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS)
- Enhanced sensors for more precise vehicle control
- Adaptation for electric and autonomous vehicles
7.3. Final Thoughts
ABS has revolutionized vehicle safety since its introduction. As automotive technology advances, we can expect ABS to become even more sophisticated, further reducing accidents and saving lives on the road.
ABS Impact on Road Safety
| Aspect | Without ABS | With ABS |
|---|---|---|
| Stopping Distance | Longer | Shorter |
| Steering Control | Limited | Maintained |
| Skidding Risk | High | Low |
| Overall Safety | Lower | Higher |
7.4. Importance of Driver Education
While ABS significantly improves vehicle safety, it’s crucial for drivers to understand how to use it effectively:
- Maintain firm, consistent pressure on the brake pedal
- Steer around obstacles while braking
- Practice emergency braking in a safe environment
- Recognize the pulsing sensation in the brake pedal during ABS activation
By combining advanced ABS technology with proper driver education, we can maximize the safety benefits of this innovative system. As vehicles become increasingly complex, staying informed about safety features like ABS is more important than ever for all road users.
8. FAQs
FAQ 1: What is ABS and how does it work?
ABS stands for Anti-lock Braking System. It’s a safety feature that prevents wheels from locking up during sudden braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. The system uses sensors to detect wheel speed and modulates brake pressure accordingly.
FAQ 2: Is ABS standard in all new vehicles?
While ABS is increasingly common, it’s not yet standard in all new vehicles. However, many countries require ABS in new cars. Check with your local regulations or dealership for specific information about ABS requirements in your area.
FAQ 3: Can ABS prevent all skidding?
ABS significantly reduces skidding but cannot prevent it entirely. It’s most effective on dry, paved surfaces and may have limited effectiveness on loose gravel or snow.
FAQ 4: How do I know if my ABS is working?
Most vehicles have an ABS warning light on the dashboard. If this light stays on, it may indicate a problem with the system. You might also feel a pulsing in the brake pedal during hard braking, which is normal ABS operation.
FAQ 5: Does ABS reduce stopping distance?
ABS can reduce stopping distance on some surfaces, particularly wet roads. However, its primary function is to maintain steering control during emergency braking.
FAQ 6: Can I pump the brakes with ABS?
No, you shouldn’t pump the brakes with ABS. The system does this automatically. In an emergency, apply firm, steady pressure to the brake pedal and let ABS do its job.
FAQ 7: How often should ABS be serviced?
ABS doesn’t require regular maintenance, but it should be checked during routine brake inspections. If the ABS warning light comes on, have the system checked by a professional immediately.
FAQ 8: Can ABS fail?
Like any mechanical system, ABS can fail. If this happens, your regular brakes will still work, but you’ll lose the anti-lock function. Always have ABS issues addressed promptly.
FAQ 9: Is driving with ABS different from driving without it?
Driving techniques are generally the same with or without ABS. However, with ABS, you don’t need to pump the brakes in emergencies. Instead, apply steady pressure and focus on steering.
FAQ 10: Can I retrofit my older car with ABS?
While technically possible, retrofitting an older car with ABS is complex and expensive. It’s generally not recommended unless done by a specialized professional.
| ABS Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Prevents wheel lock | Maintains steering control |
| Modulates brake pressure | Optimizes braking efficiency |
| Works automatically | Reduces driver error in emergencies |
| Effective on various surfaces | Improves safety in different conditions |
Now that we’ve addressed these common questions about ABS, you should have a clearer understanding of this crucial safety feature. Remember, while ABS is a valuable tool, it’s no substitute for safe driving practices and regular vehicle maintenance.
Anti-lock braking systems have revolutionized vehicle safety, providing drivers with enhanced control and stability during emergency braking situations. From its inception to modern iterations, ABS technology has continuously evolved, adapting to various driving conditions and vehicle types. The benefits of ABS, including reduced stopping distances and improved steering control, make it an indispensable feature in modern automobiles.
As vehicle owners, it’s crucial to understand the importance of maintaining your ABS system. Regular checks and timely repairs ensure optimal performance, allowing you to make the most of this life-saving technology. Whether you’re navigating slippery roads or facing unexpected obstacles, a well-functioning ABS can be the difference between a close call and a potential accident. Embrace this innovative safety feature and drive with confidence, knowing that your vehicle is equipped with a system designed to keep you safe on the road.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone