1. Introduction to Fuel Supply Systems
1.1. Definition and Purpose
Hey there, car enthusiasts and curious minds! Let’s talk about fuel supply systems. These nifty setups are like the circulatory system of your car, making sure the engine gets the fuel it needs to keep you cruising down the road. Their main job? To store fuel safely and deliver it to the engine efficiently.
1.2. Components Overview

A typical fuel supply system includes:
- Fuel tank
- Fuel pump
- Fuel lines
- Fuel filter
- Fuel injectors or carburetor
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
Each part plays a crucial role in getting fuel from the tank to your engine.
1.3. Evolution of Fuel Supply Systems
Fuel systems have come a long way! From basic gravity-fed systems in early cars to today’s high-tech, computer-controlled setups. It’s amazing to think about how much they’ve changed.
Read more about lubrication system click on this link: Lubrication System
2. Fuel Tanks and Storage

2.1. Tank Design and Materials
Modern fuel tanks are typically made of high-density polyethylene or steel. They’re designed to be tough and resistant to corrosion. Some even have special coatings to prevent fuel vapors from escaping.
2.2. Capacity and Placement
Tank size varies depending on the vehicle. Most cars have tanks that hold between 12 to 18 gallons. The placement is usually under the rear seats or in the trunk area for safety reasons.
2.3. Safety Features and Regulations
Safety is a big deal with fuel tanks. They have features like:
- Anti-spill valves
- Reinforced structures
- Leak detection systems
Regulations require fuel tanks to withstand certain crash tests without leaking. It’s reassuring to know there’s so much thought put into keeping us safe!
Read more about engine click on this link: Engine
3. Fuel Pumps: The Heart of the System
3.1. Types of Fuel Pumps

There are two main types of fuel pumps:
- Mechanical pumps (older vehicles)
- Electric pumps (most modern vehicles)
Electric pumps are more common now because they’re more reliable and efficient.
3.2. Pump Operation and Pressure Regulation
Fuel pumps create pressure to move fuel from the tank to the engine. The pressure is carefully regulated to ensure the right amount of fuel reaches the engine. Abnormal pressure can cause problems.
3.3. Common Issues and Maintenance
Fuel pumps can wear out over time. Signs of a failing pump include:
- Engine sputtering
- Loss of power
- Difficulty starting
Regular maintenance, like keeping your fuel tank at least a quarter full, can help extend your pump’s life. I learned this the hard way after running my first car on fumes one too many times!
Read more about PRV Valve click on this link: PRV Valve
4. Fuel Lines and Filters

4.1. Fuel Line Materials and Design
Fuel lines are generally made of rubber or metal. They need to be flexible yet strong to handle the pressure and resist corrosion. The design ensures fuel flows smoothly without air bubbles.
4.2. Types of Fuel Filters
There are two main types of fuel filters:
- In-line filters
- In-tank filters
Both types catch dirt and debris before it reaches your engine.
4.3. Importance of Regular Filter Replacement
Changing your fuel filter regularly is crucial. A clogged filter can starve your engine of fuel, leading to poor performance. Most mechanics recommend changing it every 20,000 to 40,000 miles, but check your car’s manual to be sure.
Read more about engine oil click on this link: Engine Oil
5. Fuel Injectors and Carburetors

5.1. Fuel Injection Systems: Types and Operation
Modern cars use fuel injection systems. There are several types:
- Port fuel injection
- Direct injection
- Sequential fuel injection
These systems spray a fine mist of fuel directly into the engine, allowing for precise control and better efficiency.
5.2. Carburetor Function and Components
Carburetors are older technology, mostly found in classic cars now. They mix air and fuel before it enters the engine. While they’re simpler, they’re not as efficient as fuel injection systems.
5.3. Injection vs. Carburetion: Pros and Cons
Fuel injection offers better fuel economy and performance, but carburetors are simpler and easier to work on. I have fond memories of tinkering with the carburetor on my first car, but I don’t miss the hassle of constant adjustments!
Get more about automobile system visit website: Autobiography Zone
6. Electronic Control Units (ECUs) in Fuel Systems

6.1. Role of ECUs in Fuel Management
ECUs are like the brain of your car’s fuel system. They control how much fuel is delivered based on various factors like engine speed, temperature, and driving conditions.
6.2. Sensors and Feedback Mechanisms
ECUs rely on sensors throughout the engine to make decisions. These include:
- Oxygen sensors
- Mass airflow sensors
- Temperature sensors
The ECU uses this information to adjust fuel delivery in real-time.
6.3. Troubleshooting ECU-related Issues
When the ECU detects a problem, it usually triggers the “Check Engine” light. While this can be frustrating, it’s actually helpful for diagnosing issues early. Many auto parts stores offer free diagnostic scans that can give you a starting point for troubleshooting.
7. Alternative Fuel Systems
7.1. LPG and CNG Systems
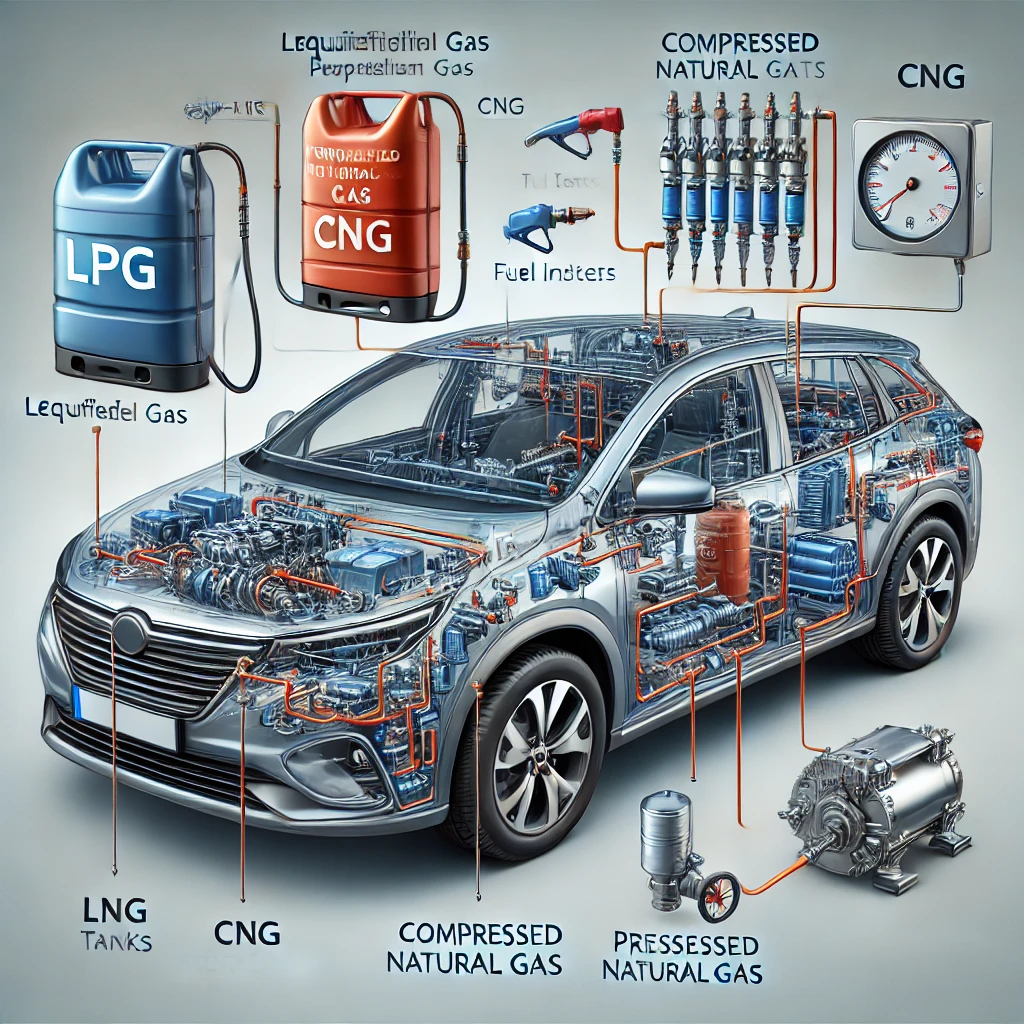
Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) and Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) systems are becoming more popular. They often require modifications to the fuel system but can offer lower emissions and fuel costs.
7.2. Biofuel Compatibility
Many modern vehicles are compatible with biofuels like ethanol blends. However, it’s important to check your owner’s manual before using these alternative fuels.
7.3. Electric and Hybrid Fuel Systems

Electric and hybrid vehicles are changing the game. They use battery systems instead of or in addition to traditional fuel systems. It’s exciting to see how quickly this technology is advancing!
8. Maintenance and Troubleshooting
8.1. Regular Maintenance Schedule
Regular maintenance is key to keeping your fuel system healthy. This includes:
- Changing fuel filters
- Checking for leaks
- Cleaning fuel injectors
Following your car’s recommended maintenance schedule can save you a lot of headaches down the road.
8.2. Common Fuel System Problems
Some common issues include:
- Clogged fuel injectors
- Failing fuel pumps
- Contaminated fuel
Pay attention to changes in your car’s performance, as these can be early signs of fuel system problems.
8.3. DIY vs. Professional Repairs
While some maintenance tasks like changing a fuel filter can be DIY projects, many fuel system repairs are best left to professionals. Safety should always come first when dealing with fuel systems.
9. Future of Fuel Supply Systems
9.1. Emerging Technologies
The future of fuel systems is exciting! We’re seeing advancements like:
- More efficient direct injection systems
- Hydrogen fuel cell technology
- Improved hybrid systems
It’s amazing to think about how different cars might be in just a few years.
9.2. Environmental Considerations
Environmental concerns are driving many changes in fuel systems. We’re seeing a push for cleaner-burning fuels and more efficient delivery systems to reduce emissions.
9.3. Regulatory Trends
Regulations are becoming stricter regarding fuel efficiency and emissions. This is pushing manufacturers to innovate and improve fuel systems constantly.
10. Summary
Fuel supply systems have come a long way and continue to evolve. From the tank to the engine, each component plays a crucial role in keeping our vehicles running smoothly and efficiently. As we look to the future, it’s clear that fuel systems will continue to change, driven by technology, environmental concerns, and regulations.
11. FAQs
- How often should I change my fuel filter? Generally every 20,000 to 40,000 miles, but check your owner’s manual for specific recommendations.
- Can I mix different types of fuel in my tank? It’s best to stick with the fuel type recommended by your vehicle manufacturer.
- What causes a fuel pump to fail? Common causes include contaminated fuel, running the tank too low, and normal wear and tear.
- How can I improve my car’s fuel efficiency? Regular maintenance, proper tire inflation, and smooth driving habits can all help improve fuel efficiency.
- Is premium fuel better for my car? Only use premium fuel if your car requires it. For most vehicles, regular fuel is just fine.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone