
Have you ever found yourself fumbling with complicated buttons or touchscreens, wishing for a simpler way to control your devices? Enter the rotary switch – a classic yet powerful solution that’s been quietly revolutionizing user interfaces for decades. 🔄
From vintage radios to modern appliances, rotary switches offer an intuitive and tactile experience that’s hard to beat. But what exactly are these circular marvels, and why should you care? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive into the world of rotary switches, exploring their types, advantages, and best practices. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast, a DIY hobbyist, or simply curious about the gadgets around you, you’re in for a fascinating journey through the ins and outs of this essential component.
Get ready to spin through eight key aspects of rotary switches, from understanding their basic principles to uncovering the latest innovations in switch technology. We’ll also address the top 10 frequently asked questions, ensuring you’ll become a rotary switch expert by the end of this post. So, grab your favorite beverage, settle in, and let’s start turning the dial on your knowledge of rotary switches! 🔧💡
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Understanding Rotary Switches
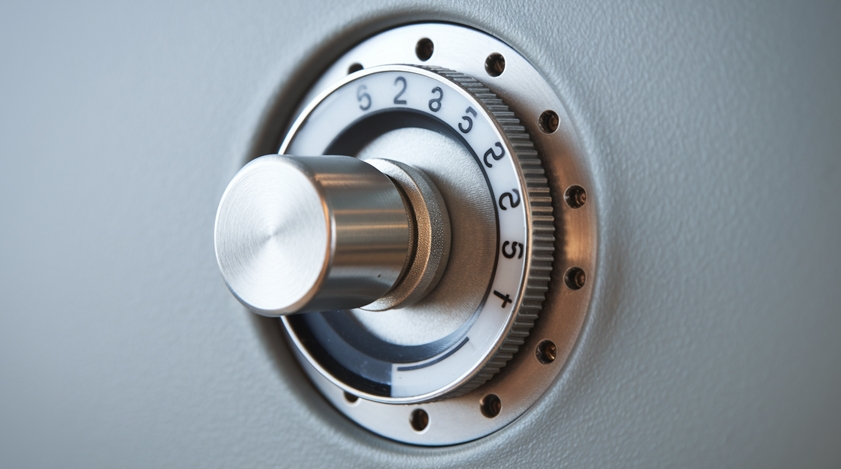

Definition and basic function
A rotary switch is a versatile electromechanical device used to control electrical circuits by rotating a knob or dial. Its primary function is to select one of multiple possible positions, each corresponding to a different circuit configuration. This allows users to choose from various predetermined settings or functions with a simple twist.
Rotary switches operate on a make-before-break principle, ensuring a smooth transition between positions without interrupting the circuit. This feature makes them ideal for applications requiring continuous power or signal flow during switching operations.
Key components of a rotary switch
A typical rotary switch consists of several essential components that work together to provide reliable and precise switching functionality:
- Rotor: The central, rotating part of the switch
- Stator: The stationary part containing contact points
- Contacts: Conductive elements that connect or disconnect circuits
- Detent mechanism: Provides tactile feedback and position stability
- Shaft: Connects the knob to the rotor
- Housing: Protects internal components and provides mounting options
Here’s a breakdown of these components and their functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Rotor | Rotates to connect different contacts |
| Stator | Houses fixed contacts and provides a base for the rotor |
| Contacts | Conduct electricity between circuits when connected |
| Detent mechanism | Ensures accurate positioning and prevents accidental switching |
| Shaft | Allows user interaction and transmits rotational force |
| Housing | Protects internal parts and facilitates mounting |
Common applications in electronics
Rotary switches find widespread use in various electronic applications due to their versatility and reliability. Some common applications include:
- Audio equipment:
- Volume control
- Input source selection
- Equalizer settings
- Industrial control panels:
- Machine operation mode selection
- Process control parameter adjustment
- Safety system activation
- Automotive systems:
- HVAC controls
- Lighting controls
- Windshield wiper speed selection
- Test and measurement equipment:
- Range selection in multimeters
- Function selection in oscilloscopes
- Calibration settings in precision instruments
- Home appliances:
- Washing machine cycle selection
- Oven temperature control
- Fan speed adjustment
Rotary switches excel in applications requiring multiple discrete settings, intuitive user interfaces, and robust performance in various environments. Their ability to handle different voltage and current ratings, coupled with their durability, makes them a popular choice for both consumer and industrial electronics.
As we move forward, we’ll explore the various types of rotary switches available, each designed to meet specific requirements in different applications.
Types of Rotary Switches

Single-pole rotary switches
Single-pole rotary switches are the simplest and most common type of rotary switch. These switches have one input (pole) and multiple output positions (throws). They are ideal for applications that require switching between different circuits or functions without the need for complex wiring.
Key features of single-pole rotary switches include:
- Simple design
- Cost-effective
- Suitable for low to medium current applications
- Available in various configurations (e.g., 1P2T, 1P3T, 1P4T, etc.)
| Configuration | Description | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 1P2T | One pole, two throws | On/Off control |
| 1P3T | One pole, three throws | Fan speed control |
| 1P4T | One pole, four throws | Light dimming |
Multi-pole rotary switches
Multi-pole rotary switches are more complex than their single-pole counterparts, offering greater versatility and functionality. These switches have multiple poles (inputs) and multiple throws (output positions), allowing for simultaneous switching of multiple circuits.
Advantages of multi-pole rotary switches:
- Increased flexibility
- Ability to control multiple circuits simultaneously
- Suitable for high-current applications
- Ideal for complex systems and equipment
Common configurations include 2P3T, 3P4T, and 4P5T, with the first number indicating the number of poles and the second number representing the number of throws.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Rotary DIP switches
Rotary DIP (Dual In-line Package) switches are specialized rotary switches designed for printed circuit board (PCB) applications. These compact switches are typically used for setting device configurations, addresses, or operating modes in electronic equipment.
Key characteristics of rotary DIP switches:
- Small form factor
- PCB mountable
- Available in various positions (4, 8, 10, 16)
- Often used in binary-coded decimal (BCD) applications
Coded rotary switches
Coded rotary switches are advanced switches that output a specific code or signal based on their position. These switches are commonly used in industrial control systems, telecommunications equipment, and test instrumentation.
Types of coded rotary switches:
- Binary-coded switches
- Gray-coded switches
- Decimal-coded switches
Advantages of coded rotary switches:
- Precise position encoding
- Reduced wiring complexity
- Simplified interface with digital systems
- Enhanced reliability in noisy environments
| Code Type | Description | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Binary | Outputs standard binary code | Easy integration with digital systems |
| Gray | Outputs Gray code (single bit change between positions) | Minimizes errors during switching |
| Decimal | Outputs decimal-coded signals | Intuitive for human operators |
Now that we’ve explored the various types of rotary switches, let’s move on to the advantages of using these versatile components in your projects and applications.
Advantages of Using Rotary Switches

Simplicity and reliability
Rotary switches are renowned for their straightforward design and dependable operation. Unlike complex electronic interfaces, rotary switches offer a user-friendly mechanism that’s easy to understand and operate. This simplicity translates to fewer potential points of failure, making rotary switches an excellent choice for applications where reliability is paramount.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Simple mechanism | Easy to use and understand |
| Fewer components | Reduced risk of malfunction |
| Mechanical operation | Less susceptible to electronic failures |
Space-saving design
One of the key advantages of rotary switches is their compact form factor. These switches can control multiple circuits or functions within a single, space-efficient package. This characteristic makes them ideal for applications where panel space is at a premium, such as in automotive dashboards, industrial control panels, or compact electronic devices.
Multiple circuit control
Rotary switches excel in their ability to control multiple circuits or functions with a single switch. This capability is particularly useful in applications that require sequential operations or the selection of various modes. For instance:
- Audio equipment: Selecting input sources
- Industrial machinery: Choosing operating modes
- Test equipment: Switching between measurement ranges
Tactile feedback for users
The physical rotation of a rotary switch provides immediate and unmistakable tactile feedback to the user. This feedback is crucial in environments where visual confirmation may be difficult or impossible, such as:
- Dark or low-light conditions
- Noisy environments where audible feedback is ineffective
- Situations requiring operation without looking at the switch
The distinct “click” felt when rotating the switch between positions ensures that users can confidently operate the device without uncertainty.
Long-term durability
Rotary switches are built to last, offering exceptional durability even in harsh environments. Their robust construction typically includes:
- High-quality materials resistant to wear and tear
- Sealed designs to protect against dust and moisture
- Mechanical components designed for millions of operations
This durability makes rotary switches an excellent choice for applications requiring long-term reliability and minimal maintenance.
| Environment | Rotary Switch Advantage |
|---|---|
| Industrial | Resistant to vibration and shock |
| Outdoor | Weather-resistant options available |
| High-traffic | Can withstand frequent use |
With these advantages in mind, it’s clear why rotary switches remain a popular choice across various industries and applications. Their combination of simplicity, reliability, and versatility makes them an invaluable component in many electronic and mechanical systems. Next, we’ll explore how to select the right rotary switch for your specific needs, ensuring you can leverage these advantages effectively in your projects.
Selecting the Right Rotary Switch

Considering voltage and current ratings
When selecting a rotary switch, one of the most critical factors to consider is the voltage and current ratings. These ratings determine the switch’s capacity to handle electrical loads safely and efficiently. Let’s break down the importance of these ratings:
| Rating | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage | Maximum voltage the switch can handle | Prevents arcing and insulation breakdown |
| Current | Maximum current the switch can carry | Prevents overheating and contact degradation |
To choose the right rotary switch, always ensure that its voltage and current ratings exceed the maximum requirements of your application. It’s recommended to select a switch with ratings at least 20% higher than your circuit’s needs to provide a safety margin.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Evaluating the number of positions needed
The number of positions in a rotary switch is crucial for meeting your application’s functionality requirements. Consider the following:
- Single-pole switches: Typically offer 2 to 12 positions
- Multi-pole switches: Can have up to 24 positions
When evaluating positions, consider:
- The number of distinct settings your application requires
- Future expansion needs
- User interface simplicity
Remember, more positions aren’t always better. Choose a switch with just enough positions to meet your needs while maintaining ease of use.
Choosing between make-before-break and break-before-make
The contact action of a rotary switch is another critical consideration. The two main types are:
- Make-before-break (MBB):
- New contact is made before the previous one breaks
- Ensures continuous circuit connection
- Ideal for applications where momentary interruptions are unacceptable
- Break-before-make (BBM):
- Existing contact breaks before the new one is made
- Prevents short circuits between adjacent contacts
- Suitable for applications where momentary disconnections are acceptable
Choose MBB for continuous power applications and BBM for switching between mutually exclusive options.
Assessing environmental factors
The environment in which your rotary switch will operate plays a significant role in its selection. Consider these factors:
- Temperature range: Ensure the switch can withstand both high and low temperature extremes in your application.
- Humidity: Look for switches with appropriate sealing if operating in high-humidity environments.
- Dust and debris: Consider sealed switches for dusty or dirty environments.
- Vibration and shock: Choose switches with robust construction for high-vibration applications.
- Chemical exposure: Select switches with appropriate materials for resistance to specific chemicals if applicable.
Here’s a quick reference table for environmental considerations:
| Environmental Factor | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Operating range, thermal cycling |
| Humidity | Sealing, corrosion resistance |
| Dust/Debris | IP rating, sealed construction |
| Vibration/Shock | Mechanical durability, mounting style |
| Chemical Exposure | Material compatibility |
By carefully considering these factors – voltage and current ratings, number of positions, contact action, and environmental conditions – you’ll be well-equipped to select the right rotary switch for your specific application. Remember, the goal is to choose a switch that not only meets your current needs but also provides room for future expansion and ensures long-term reliability in your intended operating environment.
Installation and Wiring Best Practices

Proper mounting techniques
When installing rotary switches, proper mounting is crucial for optimal performance and longevity. Begin by selecting an appropriate location that allows easy access and operation. Ensure the mounting surface is clean, dry, and free from debris. Use the following techniques for secure mounting:
- Panel mounting: Most common for rotary switches
- PCB mounting: For switches designed for circuit board integration
- Surface mounting: For specialized applications
| Mounting Type | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Panel | Easy access, versatile | Requires panel cutout |
| PCB | Space-efficient, direct integration | Limited to PCB-specific switches |
| Surface | Minimal intrusion, quick installation | May require additional protection |
Always consult the manufacturer’s specifications for hole sizes and clearance requirements. Use appropriate tools, such as a drill or punch, to create clean, precise holes. Secure the switch using the provided hardware, taking care not to overtighten and potentially damage the switch or panel.
Correct wiring procedures
Proper wiring is essential for the safe and efficient operation of rotary switches. Follow these steps to ensure correct wiring:
- Identify switch terminals and their functions
- Choose appropriate wire gauge based on current requirements
- Strip wire insulation to the correct length
- Secure connections using crimp terminals or soldering
- Implement proper strain relief to prevent wire damage
When connecting wires, pay close attention to the switch’s terminal arrangement. Many rotary switches use a common terminal with multiple positions, so ensure you’re connecting to the correct poles and throws. Use heat shrink tubing or electrical tape to insulate exposed connections and prevent short circuits.
Avoiding common installation errors
To ensure a successful rotary switch installation, be aware of and avoid these common errors:
- Misalignment during mounting
- Incorrect wiring sequence
- Inadequate insulation between terminals
- Failure to account for environmental factors
One frequent mistake is neglecting to consider the switch’s rotation direction and stop positions. Always verify that the switch aligns properly with any associated markings or indicators on the panel or equipment.
Another critical aspect is proper grounding. Ensure that any metal components, including the switch housing if applicable, are correctly grounded to prevent electrical hazards and interference.
When working with multiple switches or complex circuits, use color-coded wires and clear labeling to minimize confusion and potential wiring errors. Document your wiring scheme for future reference and maintenance.
Now that we’ve covered the best practices for installation and wiring, it’s important to understand how to maintain and troubleshoot rotary switches to ensure their longevity and reliable operation.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting

Regular cleaning and inspection
Proper maintenance of rotary switches is crucial for ensuring their longevity and reliable operation. Regular cleaning and inspection should be an integral part of your maintenance routine. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you keep your rotary switches in top condition:
- Power off: Always disconnect the power source before performing any maintenance.
- Visual inspection: Look for signs of wear, damage, or corrosion.
- Dust removal: Use compressed air to blow away dust and debris.
- Contact cleaning: Apply contact cleaner to remove oxidation and residue.
- Lubrication: Apply a thin layer of suitable lubricant to moving parts.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency | Tools Required |
|---|---|---|
| Visual inspection | Monthly | None |
| Dust removal | Quarterly | Compressed air can |
| Contact cleaning | Semi-annually | Contact cleaner, lint-free cloth |
| Lubrication | Annually | Suitable lubricant, applicator |
Diagnosing switch failures
When a rotary switch malfunctions, identifying the root cause is essential for effective troubleshooting. Common issues and their potential causes include:
- Intermittent contact: Often due to dirt, oxidation, or loose connections
- Stiff rotation: May indicate worn detents or lack of lubrication
- No switching action: Possibly caused by broken internal components or severe contamination
To diagnose these issues:
- Check for visible damage or contamination
- Test continuity using a multimeter
- Verify proper alignment of switch components
- Inspect wiring connections for looseness or corrosion
Replacing faulty switches
When troubleshooting efforts fail to resolve the issue, replacing the faulty switch becomes necessary. Follow these steps for a successful replacement:
- Document the current wiring configuration, including wire colors and terminal positions
- Remove the old switch, taking care not to damage surrounding components
- Compare the new switch with the old one to ensure compatibility
- Install the new switch, making sure it’s securely mounted
- Reconnect the wires according to your documentation
- Test the new switch thoroughly before restoring power to the system
Remember that proper disposal of the old switch is important, especially if it contains hazardous materials. Always consult local regulations for guidance on electronic waste disposal.
By following these maintenance, troubleshooting, and replacement procedures, you can significantly extend the life of your rotary switches and minimize downtime due to switch failures. Regular attention to these components ensures smooth operation and reliable performance in your electrical systems.
Innovations in Rotary Switch Technology
Digital rotary encoders
Digital rotary encoders represent a significant leap forward in rotary switch technology. These devices convert rotational movement into digital signals, offering enhanced precision and reliability compared to traditional mechanical switches.
Key features of digital rotary encoders include:
- High resolution
- Increased durability
- Compatibility with digital systems
- Accurate position tracking
Here’s a comparison between traditional rotary switches and digital rotary encoders:
| Feature | Traditional Rotary Switch | Digital Rotary Encoder |
|---|---|---|
| Output | Analog | Digital |
| Resolution | Limited by physical detents | High (up to thousands of positions) |
| Wear and tear | Mechanical parts prone to wear | Reduced mechanical wear |
| Lifespan | Moderate | Extended |
| Compatibility | Analog systems | Digital and analog systems |
Touchless rotary switches
Touchless rotary switches represent another innovative advancement in the field. These switches operate without physical contact, utilizing technologies such as:
- Hall effect sensors
- Optical sensors
- Capacitive sensing
Benefits of touchless rotary switches include:
- Elimination of mechanical wear
- Resistance to environmental factors (dust, moisture)
- Improved hygiene for medical and food industry applications
- Enhanced user experience
Integration with smart systems
The integration of rotary switches with smart systems has opened up new possibilities for control and automation. This innovation allows rotary switches to:
- Connect to IoT (Internet of Things) devices
- Interact with mobile applications
- Provide remote control capabilities
- Offer programmable functions
Smart rotary switches can be found in various applications, including:
- Home automation systems
- Industrial control panels
- Automotive interfaces
- Audio equipment
These advanced rotary switches often feature:
- Customizable LED indicators
- Haptic feedback
- Wireless connectivity (Bluetooth, Wi-Fi)
- Integration with voice assistants
As we continue to see advancements in technology, rotary switches are evolving to meet the demands of modern applications. The combination of traditional tactile feedback with cutting-edge digital capabilities is creating more versatile and user-friendly control interfaces. Next, we’ll address some frequently asked questions about rotary switches to help you better understand their use and application in various scenarios.
10 FAQs

What is a rotary switch?
A rotary switch is an electromechanical device used to select one of several possible positions by rotating a knob or dial. It consists of a spindle or shaft with a contact arm that moves between different stationary contacts, allowing the user to choose from multiple circuit options.
How does a rotary switch differ from a toggle switch?
| Feature | Rotary Switch | Toggle Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Operation | Rotational movement | Up/down or side-to-side movement |
| Number of positions | Multiple (typically 3 or more) | Usually 2-3 positions |
| Flexibility | Can accommodate more circuit options | Limited to fewer options |
| Space efficiency | Compact for multiple selections | Takes up more panel space for multiple switches |
| Visual feedback | Clear indication of selected position | May require additional indicators |
What are the common applications of rotary switches?
Rotary switches are widely used in various applications, including:
- Audio equipment (volume control, input selection)
- Industrial machinery (mode selection, speed control)
- Automotive systems (headlight controls, HVAC settings)
- Home appliances (washing machine cycle selection)
- Test and measurement equipment
- Military and aerospace systems
How long do rotary switches typically last?
The lifespan of a rotary switch depends on various factors, including quality, usage frequency, and environmental conditions. High-quality rotary switches can last for millions of rotations or several decades with proper maintenance.
Are rotary switches suitable for high-current applications?
While most rotary switches are designed for low to medium current applications, there are heavy-duty rotary switches available for high-current scenarios. It’s crucial to check the switch’s specifications and choose one rated for the intended current load.
Can rotary switches be used in hazardous environments?
Yes, there are specially designed rotary switches for hazardous environments. These switches are sealed, explosion-proof, and comply with relevant safety standards for use in potentially explosive atmospheres.
How do I clean a rotary switch?
To clean a rotary switch:
- Disconnect power
- Use compressed air to remove dust
- Apply contact cleaner spray
- Rotate the switch through all positions
- Allow to dry before reconnecting power
Always consult the manufacturer’s instructions before cleaning.
What is the difference between make-before-break and break-before-make rotary switches?
| Type | Description | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Make-before-break | New contact is made before breaking the old one | Ensures continuous connection, useful in some audio applications |
| Break-before-make | Old contact is broken before making the new one | Prevents short circuits, ideal for most electrical applications |
Can rotary switches be customized?
Many manufacturers offer customization options for rotary switches, including:
- Number of positions
- Contact materials
- Shaft length and style
- Mounting options
- Special markings or colors
How do I troubleshoot a faulty rotary switch?
To troubleshoot a rotary switch:
- Check for visible damage or contamination
- Test continuity with a multimeter in each position
- Verify proper alignment of contacts
- Inspect for loose connections or worn parts
- Clean the switch if necessary
- Replace the switch if issues persist
If the problem continues, consult a professional or the manufacturer for further assistance.

Rotary switches offer a versatile and reliable solution for controlling electrical circuits in various applications. From simple on/off functions to complex multi-position selections, these devices provide precise control and durability. By understanding the different types, advantages, and selection criteria, you can choose the perfect rotary switch for your specific needs.
Proper installation, wiring, and maintenance are crucial for ensuring optimal performance and longevity of rotary switches. As technology advances, innovations in rotary switch design continue to expand their capabilities and applications. Whether you’re working on a DIY project or designing an industrial control system, rotary switches remain an essential component in the world of electrical engineering and electronics.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone


