
Have you ever found yourself stranded in a parking lot, desperately turning your key only to hear that dreaded clicking sound? 🔑😰 It’s a scenario that sends chills down every driver’s spine. The culprit? Often, it’s a faulty self-starter motor. This tiny yet crucial component is the unsung hero of your vehicle, responsible for bringing your engine to life with just a turn of the key.
But what exactly is a self-starter motor, and how does it work its magic? 🧐 Whether you’re a car enthusiast or simply want to understand your vehicle better, diving into the world of self-starter motors can be fascinating. From their intricate mechanics to the latest technological advancements, there’s a lot to uncover about these powerful little devices.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll take you on a journey through the ins and outs of self-starter motors. We’ll explore their inner workings, examine different types, troubleshoot common issues, and even peek into the future of starter technology. So, buckle up and get ready to become a self-starter motor expert! 🚗💨
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Understanding Self Starter Motors
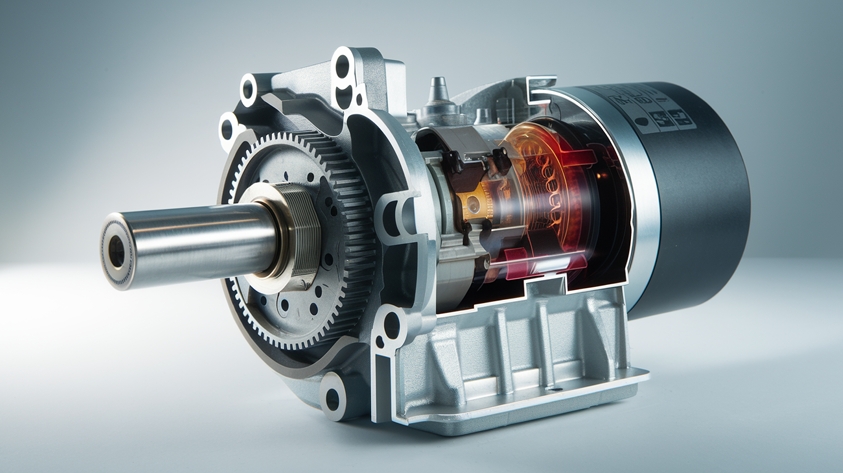
Definition and basic function
A self starter motor, also known as an electric starter or simply a starter, is an essential component in modern vehicles that initiates the engine’s operation. Its primary function is to convert electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy, which then rotates the engine’s crankshaft to start the combustion process.
When you turn the ignition key or press the start button in your vehicle, the self starter motor engages, providing the initial torque required to overcome the engine’s compression and friction. This action allows the engine to begin its cycle independently, eliminating the need for manual cranking methods used in early automobiles.
Key components
The self starter motor consists of several crucial components that work together to ensure smooth and reliable engine starting. Here’s a breakdown of the key elements:
- Electric motor: The core of the starter, responsible for converting electrical energy into rotational motion.
- Solenoid: An electromagnetic switch that engages the starter drive with the engine’s flywheel.
- Starter drive: Also known as a Bendix drive, it connects the starter motor to the engine’s flywheel.
- Commutator: Ensures proper current flow through the motor’s armature windings.
- Brushes: Conduct electricity from the battery to the commutator.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Electric motor | Converts electrical energy to mechanical energy |
| Solenoid | Engages starter drive with flywheel |
| Starter drive | Connects starter motor to flywheel |
| Commutator | Manages current flow in armature windings |
| Brushes | Conduct electricity from battery to commutator |
Advantages over traditional starters
Self starter motors offer numerous benefits compared to their predecessors, making them the standard in modern vehicles:
- Convenience: Eliminates the need for manual cranking, making vehicle starting effortless and accessible to all drivers.
- Safety: Reduces the risk of injury associated with manual cranking methods.
- Reliability: Provides consistent starting performance across various weather conditions and engine states.
- Efficiency: Enables quick engine starts, reducing fuel consumption and emissions during the starting process.
- Compatibility: Works seamlessly with modern engine management systems and electronic controls.
The introduction of self starter motors revolutionized the automotive industry, significantly improving the user experience and overall vehicle performance. As we delve deeper into how these essential components operate, you’ll gain a better understanding of their crucial role in modern vehicles.
How Self Starter Motors Work
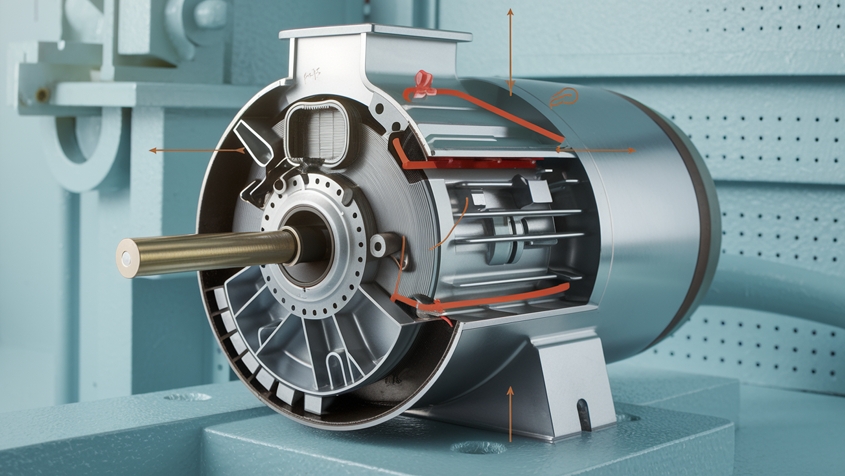
Engaging the flywheel
The self-starter motor’s primary function begins with engaging the flywheel. This crucial step initiates the engine starting process. When you turn the ignition key or press the start button, an electrical signal is sent to the starter motor, activating its solenoid.
The solenoid then pushes out a small gear called the pinion gear, which meshes with the larger flywheel gear attached to the engine’s crankshaft. This engagement creates a mechanical connection between the starter motor and the engine.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Solenoid | Activates pinion gear |
| Pinion gear | Engages with flywheel |
| Flywheel | Connects to engine crankshaft |
Cranking the engine
Once the pinion gear is engaged with the flywheel, the starter motor begins to rotate. This rotation transfers power from the electric motor to the engine’s crankshaft through the flywheel. The cranking process involves:
- Rapid rotation of the crankshaft
- Movement of pistons within cylinders
- Compression of air-fuel mixture
- Creation of conditions necessary for combustion
The starter motor must overcome the engine’s compression and friction to achieve the minimum cranking speed required for ignition. This speed varies depending on the engine type but typically ranges from 200 to 300 RPM.
Disengaging after ignition
After the engine starts, the starter motor must disengage quickly to prevent damage. This process happens automatically and involves:
- Detection of engine start (usually through increased RPM)
- Deactivation of the solenoid
- Retraction of the pinion gear from the flywheel
The rapid disengagement is crucial because if the starter remained engaged, the now-running engine would spin the starter motor at dangerously high speeds, potentially causing severe damage.
Role of the solenoid
The solenoid plays a vital role in the operation of a self-starter motor. It serves as both an electrical switch and a mechanical actuator. Here are its primary functions:
- Electrical switching: The solenoid acts as a high-current relay, controlling the flow of electricity from the battery to the starter motor.
- Mechanical actuation: It moves the pinion gear into and out of engagement with the flywheel.
- Force multiplication: The solenoid’s electromagnetic field provides the necessary force to push the pinion gear against the flywheel, ensuring proper engagement.
- Timing control: It ensures that the pinion gear engages fully before allowing high current to flow to the starter motor.
| Solenoid Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrical | Controls current flow |
| Mechanical | Moves pinion gear |
| Force | Ensures proper engagement |
| Timing | Coordinates engagement and current flow |
The solenoid’s dual electrical and mechanical roles make it a critical component in the self-starter system, ensuring smooth and reliable engine starts. Its precise operation coordinates the engagement, power delivery, and disengagement processes essential for effective engine starting.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Types of Self Starter Motors
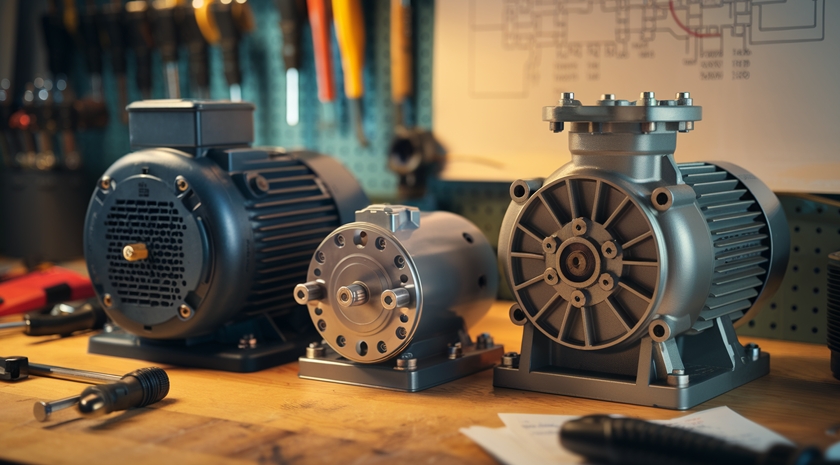

A. Gear reduction starters
Gear reduction starters are a popular type of self-starter motor widely used in modern vehicles. These starters employ a gear system to multiply the torque output, allowing for efficient engine cranking with less electrical power.
The key advantage of gear reduction starters lies in their ability to provide high torque at lower speeds. This makes them particularly suitable for larger engines or those requiring more cranking power. Let’s examine the main features and benefits of gear reduction starters:
- High torque output
- Compact size
- Reduced power consumption
- Longer lifespan
- Quieter operation
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| High torque | Easier engine starting, especially in cold weather |
| Compact size | Easier installation in tight engine compartments |
| Reduced power consumption | Less strain on the vehicle’s electrical system |
| Longer lifespan | Reduced maintenance and replacement costs |
| Quieter operation | Enhanced driver comfort |
B. Direct drive starters
Direct drive starters, also known as inertia starters, represent an older technology that’s still found in some vehicles. These starters directly engage the engine’s flywheel without any intermediate gearing.
While simpler in design, direct drive starters have some limitations:
- Lower torque output
- Higher power consumption
- Larger size
- Potentially shorter lifespan
Despite these drawbacks, direct drive starters can be suitable for smaller engines or in applications where simplicity is prioritized over efficiency.
C. Permanent magnet starters
Permanent magnet starters represent a more recent innovation in self-starter technology. These starters use powerful permanent magnets instead of wound field coils, offering several advantages:
- Lighter weight
- Improved efficiency
- Reduced power consumption
- Compact design
- Longer service life
Here’s a comparison of the three starter types:
| Feature | Gear Reduction | Direct Drive | Permanent Magnet |
|---|---|---|---|
| Torque output | High | Low | Medium to High |
| Size | Compact | Large | Very Compact |
| Weight | Medium | Heavy | Light |
| Efficiency | High | Low | Very High |
| Power consumption | Low | High | Very Low |
| Lifespan | Long | Medium | Very Long |
Permanent magnet starters are becoming increasingly popular in modern vehicles due to their excellent balance of performance, efficiency, and durability. They’re particularly well-suited for hybrid and electric vehicles, where weight and energy efficiency are crucial factors.
When choosing a self-starter motor, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your vehicle and engine. Factors such as engine size, cranking power needs, and available space in the engine compartment all play a role in determining the most suitable starter type.
Now that we’ve explored the different types of self-starter motors, let’s move on to some common issues you might encounter with these crucial components and how to troubleshoot them effectively.
Common Issues and Troubleshooting
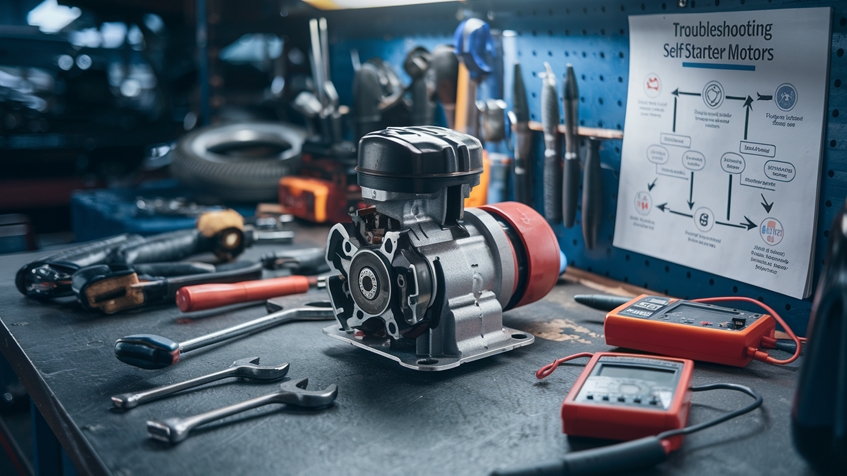

A. Clicking sound but no start
When you turn the key and hear a clicking sound without the engine starting, it’s often a sign of a weak battery or a faulty starter solenoid. This issue can be frustrating, but there are several steps you can take to diagnose and potentially resolve the problem:
- Check the battery voltage
- Inspect battery connections
- Test the starter solenoid
- Examine the starter motor
| Possible Cause | Diagnosis | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Weak battery | Battery voltage below 12.4V | Charge or replace battery |
| Loose connections | Visible corrosion or loose terminals | Clean and tighten connections |
| Faulty solenoid | Clicking sound from solenoid | Replace solenoid |
| Worn starter motor | No movement when tested directly | Replace starter motor |
B. Slow cranking
Slow cranking is often indicative of a dying battery or a worn-out starter motor. This issue can lead to difficulty starting your vehicle, especially in cold weather. Here are some troubleshooting steps:
- Test the battery’s cold cranking amps (CCA)
- Check for parasitic drain
- Inspect the starter motor brushes
- Examine the flywheel ring gear
If the battery tests well, the problem may lie with the starter motor itself. Worn brushes or a weak armature can cause slow cranking. In some cases, the flywheel ring gear may have damaged teeth, leading to poor engagement with the starter pinion gear.
C. Grinding noise during start
A grinding noise during start-up is a serious issue that requires immediate attention. This sound typically indicates a problem with the starter drive gear or the flywheel ring gear. Possible causes include:
- Misaligned starter motor
- Worn starter drive gear
- Damaged flywheel ring gear
- Stuck starter solenoid
To troubleshoot this issue:
- Inspect the starter mounting bolts for tightness
- Check the starter drive gear for wear or damage
- Examine the flywheel ring gear for missing or worn teeth
- Test the starter solenoid for proper disengagement
D. Starter stays engaged after engine starts
When the starter motor remains engaged after the engine has started, it can cause significant damage to both the starter and the flywheel. This problem is often caused by:
- Stuck starter solenoid
- Faulty ignition switch
- Worn starter drive gear
To address this issue:
- Check the ignition switch for proper operation
- Inspect the starter solenoid for signs of sticking or failure
- Examine the starter drive gear for wear or damage
- Test the starter motor’s return spring
E. Complete failure to engage
If the starter motor fails to engage at all, with no sound or movement, it could be due to several factors:
- Dead battery
- Broken or disconnected wiring
- Failed starter motor
- Faulty ignition switch
Troubleshooting steps include:
- Verify battery voltage and connections
- Inspect all wiring connections to the starter and solenoid
- Test the ignition switch for continuity
- Check for voltage at the starter motor when the key is turned
In some cases, a complete failure to engage may require professional diagnosis and repair, especially if the issue is related to the vehicle’s electrical system or computer controls.
By following these troubleshooting steps, you can often identify and resolve common self starter motor issues. However, if you’re unsure or uncomfortable performing these checks, it’s always best to consult a professional mechanic to avoid potential damage to your vehicle’s starting system.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Maintaining Your Self Starter Motor

Regular inspections
Regular inspections are crucial for maintaining the longevity and efficiency of your self starter motor. By conducting periodic checks, you can identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. Here’s a list of key areas to focus on during your inspections:
- Battery connections
- Starter solenoid
- Wiring harness
- Mounting bolts
- Brushes and commutator
To ensure a thorough inspection, follow this simple checklist:
| Inspection Item | What to Look For | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Battery connections | Corrosion, loose terminals | Monthly |
| Starter solenoid | Secure mounting, clean contacts | Quarterly |
| Wiring harness | Frayed wires, loose connections | Bi-annually |
| Mounting bolts | Tightness, signs of wear | Annually |
| Brushes and commutator | Wear, carbon buildup | Annually |
Cleaning connections
Clean connections are essential for optimal performance of your self starter motor. Over time, corrosion and dirt can accumulate on the battery terminals and other electrical connections, impeding the flow of electricity. Here’s how to keep your connections clean:
- Disconnect the battery
- Use a wire brush to remove corrosion
- Apply a baking soda and water solution to neutralize acid
- Rinse with clean water and dry thoroughly
- Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to prevent future corrosion
Lubricating moving parts
Proper lubrication of moving parts is crucial for reducing friction and wear in your self starter motor. Focus on these key components:
- Drive gear
- Armature shaft bearings
- Solenoid plunger
Use a high-quality, heat-resistant grease specifically designed for automotive applications. Apply sparingly to avoid over-lubrication, which can attract dirt and debris.
Replacing worn components
Even with regular maintenance, some components of your self starter motor will eventually wear out and require replacement. Common parts that may need replacing include:
- Brushes
- Bushings
- Solenoid contacts
- Drive gear
When replacing these components, always use high-quality, OEM-approved parts to ensure optimal performance and longevity. If you’re not comfortable performing these replacements yourself, consult a professional mechanic.
Now that we’ve covered the essential aspects of maintaining your self starter motor, let’s explore the latest advancements in self starter technology that are shaping the future of automotive starting systems.
Advancements in Self Starter Technology

Smart starters with diagnostic capabilities
In recent years, self starter motors have undergone significant advancements, particularly in the realm of smart starters with diagnostic capabilities. These innovative systems offer numerous benefits to both drivers and mechanics, revolutionizing the way we approach vehicle maintenance and troubleshooting.
Smart starters are equipped with advanced sensors and microprocessors that continuously monitor the starter motor’s performance. This real-time data collection allows for early detection of potential issues, helping to prevent unexpected breakdowns and extend the lifespan of the starter motor.
Key features of smart starters with diagnostic capabilities include:
- Performance monitoring
- Fault detection and reporting
- Predictive maintenance alerts
- Remote diagnostics
- Integration with vehicle management systems
Here’s a comparison of traditional starters vs. smart starters:
| Feature | Traditional Starter | Smart Starter |
|---|---|---|
| Diagnostics | Manual inspection | Real-time monitoring |
| Fault detection | After failure | Early warning system |
| Maintenance | Reactive | Predictive |
| Data collection | Limited | Comprehensive |
| Integration | Standalone | Connected to vehicle systems |
Integration with start-stop systems
As automotive manufacturers strive to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, start-stop systems have become increasingly popular. These systems automatically shut off the engine when the vehicle comes to a stop and restart it when the driver releases the brake pedal or engages the clutch.
Self starter motors play a crucial role in the efficient operation of start-stop systems. Modern starters designed for these applications feature:
- Enhanced durability to withstand frequent starts
- Faster engagement and disengagement
- Reduced noise and vibration
- Improved efficiency to minimize battery drain
The integration of self starter motors with start-stop systems has led to significant improvements in fuel economy, particularly in urban driving conditions where frequent stops are common.
Hybrid and electric vehicle applications
As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, self starter motors are evolving to meet the unique requirements of hybrid and electric vehicles. In these applications, the starter motor often serves multiple purposes beyond simply starting the internal combustion engine.
Key advancements in self starter technology for hybrid and electric vehicles include:
- Integration with regenerative braking systems
- Dual-function motors that serve as both starters and generators
- High-voltage starter systems for improved efficiency
- Compact designs to accommodate complex drivetrain layouts
These innovations have contributed to the overall efficiency and performance of hybrid and electric vehicles, helping to extend range and improve reliability.
As we look to the future, self starter motor technology will continue to evolve, playing a crucial role in the development of more efficient and environmentally friendly vehicles. The integration of smart diagnostics, start-stop systems, and electrification will drive further advancements in this essential automotive component.
10 FAQs

Q1: What is a self starter motor?
A self starter motor, also known simply as a starter, is an electric motor that initiates the engine’s operation in a vehicle. It’s a crucial component that allows you to start your car with the turn of a key or push of a button, eliminating the need for manual cranking.
Q2: How long does a self starter motor typically last?
The lifespan of a self starter motor can vary depending on usage and maintenance. On average, a starter motor can last between 100,000 to 150,000 miles. However, some may need replacement earlier, while others can last the entire lifetime of the vehicle.
Q3: What are the signs of a failing starter motor?
Common signs of a failing starter motor include:
- Clicking sound when turning the key
- Slow cranking
- Intermittent starting issues
- Grinding noise during start
- Smoke coming from under the hood
Q4: Can a bad battery cause starter motor problems?
Yes, a weak or dead battery can often mimic starter motor issues. Before assuming your starter is faulty, it’s important to check your battery’s condition and connections.
Q5: How much does it cost to replace a starter motor?
The cost of replacing a starter motor can vary widely depending on the vehicle make and model. Here’s a general price range:
| Vehicle Type | Average Cost Range |
|---|---|
| Compact Car | $200 – $400 |
| Midsize Car | $300 – $550 |
| Luxury Car | $500 – $1000+ |
| Truck/SUV | $350 – $600 |
These prices include both parts and labor. Always get multiple quotes from reputable mechanics.
Q6: Can I replace a starter motor myself?
While it’s possible for experienced DIY mechanics to replace a starter motor, it’s generally recommended to have a professional do the job. The process can be complex and may require special tools, especially in modern vehicles where the starter is often in a hard-to-reach location.
Q7: How can I extend the life of my starter motor?
To extend your starter motor’s life:
- Avoid excessive cranking when starting the engine
- Maintain your battery in good condition
- Keep electrical connections clean and tight
- Address any starting issues promptly
- Follow your vehicle’s maintenance schedule
Q8: Are there different types of starter motors?
Yes, there are several types of starter motors, including:
- Direct drive starters
- Gear reduction starters
- Permanent magnet starters
- Pneumatic starters (used in large engines)
Q9: Can weather affect my starter motor?
Extreme temperatures can affect starter motor performance. Cold weather can make the engine oil thicker, requiring more power from the starter. Hot weather can cause electrical components to expand, potentially leading to connection issues.
Q10: What’s the difference between a starter motor and an alternator?
While both are crucial electrical components, they serve different functions:
| Starter Motor | Alternator |
|---|---|
| Starts the engine | Charges the battery |
| Operates briefly during startup | Runs continuously while the engine is on |
| Consumes electrical power | Generates electrical power |
| Connected to the engine’s flywheel | Connected to the engine via a belt |
Understanding these differences can help in diagnosing electrical issues in your vehicle.

Self starter motors have revolutionized the way we start our vehicles, making the process effortless and efficient. From understanding their basic operation to exploring different types and troubleshooting common issues, we’ve covered the essential aspects of these crucial automotive components. Proper maintenance and staying informed about technological advancements can significantly extend the life of your self starter motor and improve overall vehicle performance.
As vehicles continue to evolve, so do self starter motors. By keeping up with the latest developments and following the maintenance tips provided, you can ensure your vehicle starts reliably every time. Whether you’re a car enthusiast or simply looking to better understand your vehicle, knowledge about self starter motors is invaluable for every driver. Remember, a well-maintained self starter motor is key to a smooth and stress-free driving experience.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone


