
Have you ever experienced that heart-stopping moment when your car’s steering suddenly feels off? 😱 It’s a scenario that sends shivers down any driver’s spine. At the heart of this crucial control system lies an often-overlooked component: the steering gear box. This unsung hero of your vehicle’s mechanics plays a pivotal role in translating your steering wheel movements into the precise direction of your wheels.
But here’s the kicker: many drivers are blissfully unaware of the steering gear box’s importance until something goes wrong. From the subtle signs of wear to the sudden loss of control, steering gear box issues can range from mildly inconvenient to downright dangerous. 🚗💨 So, buckle up as we dive into the world of steering gear boxes, exploring everything from the basics to advanced upgrades that could revolutionize your driving experience.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll steer you through the ins and outs of steering gear boxes. We’ll start by breaking down the fundamentals, compare manual and power steering systems, and highlight common problems to watch out for. You’ll also discover essential maintenance tips to keep your steering smooth and responsive, and explore exciting upgrade options for enthusiasts. Finally, we’ll address the top 10 frequently asked questions to ensure you’re fully equipped with the knowledge to keep your vehicle on the straight and narrow. Let’s turn the key and get started! 🔧🚗
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Understanding Steering Gear Box Basics

Definition and function
The steering gear box is a crucial component of a vehicle’s steering system, acting as the intermediary between the steering wheel and the wheels. Its primary function is to convert the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion, which then directs the wheels to turn left or right. This mechanism allows drivers to control the direction of their vehicle with precision and ease.
Key components
A typical steering gear box consists of several essential parts working together to ensure smooth and accurate steering:
- Input shaft
- Sector shaft
- Worm gear
- Pitman arm
- Bearings
- Housing
Here’s a breakdown of these components and their roles:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Input shaft | Connects to the steering wheel and transfers driver input |
| Sector shaft | Converts rotational motion to linear motion |
| Worm gear | Meshes with the sector gear to amplify steering force |
| Pitman arm | Connects the sector shaft to the steering linkage |
| Bearings | Reduce friction and support moving parts |
| Housing | Encloses and protects internal components |
Types of steering gear boxes
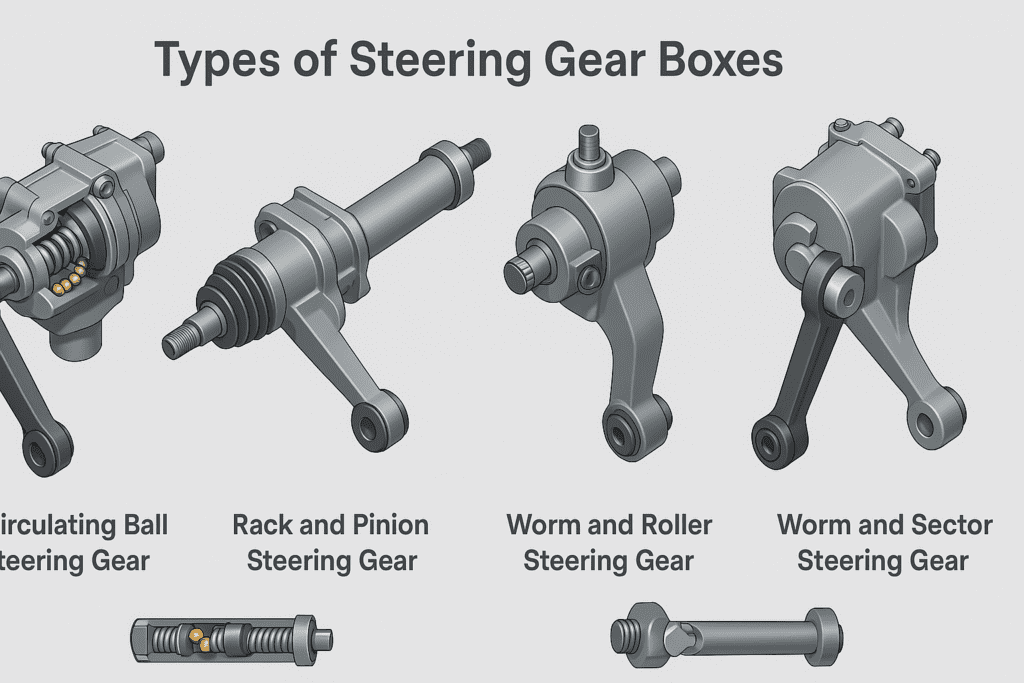
There are several types of steering gear boxes, each with its own advantages and applications:
- Recirculating ball steering gear
- Rack and pinion steering gear
- Worm and roller steering gear
- Worm and sector steering gear
The recirculating ball and rack and pinion systems are the most common in modern vehicles. Recirculating ball steering gears are often found in larger vehicles and trucks due to their ability to handle heavier loads, while rack and pinion systems are prevalent in smaller cars for their simplicity and responsiveness.
Importance in vehicle control
The steering gear box plays a vital role in vehicle control and safety:
- Precision: It allows for accurate steering inputs, enabling drivers to navigate turns and obstacles with precision.
- Force multiplication: The gear mechanism amplifies the driver’s steering effort, making it easier to turn the wheels, especially at low speeds or when stationary.
- Stability: A well-functioning steering gear box contributes to the overall stability of the vehicle, particularly during cornering and high-speed maneuvers.
- Feedback: It provides tactile feedback to the driver about road conditions and tire grip, enhancing the driving experience and safety.
Understanding the basics of steering gear boxes is essential for vehicle owners and enthusiasts alike. With this knowledge, drivers can better appreciate the complexity of their vehicle’s steering system and recognize the importance of proper maintenance. As we delve deeper into the world of steering gear boxes, we’ll explore the differences between manual and power steering systems, which build upon these fundamental concepts.
Manual vs. Power Steering Gear Boxes
Differences in operation
Manual and power steering gear boxes operate on fundamentally different principles, each with its unique mechanism. Let’s explore these differences:
| Feature | Manual Steering Gear Box | Power Steering Gear Box |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Driver’s physical effort | Engine-driven hydraulic pump or electric motor |
| Effort Required | High, especially at low speeds | Low, consistent across all speeds |
| Feedback | Direct road feel | Reduced road feel |
| Complexity | Simple mechanical system | More complex with additional components |
Manual steering gear boxes rely entirely on the driver’s input to turn the wheels. The steering wheel is directly connected to the steering rack through a series of shafts and gears. When the driver turns the wheel, this mechanical force is transmitted directly to the wheels.
In contrast, power steering gear boxes use an auxiliary power source to assist the driver’s input. This can be either a hydraulic system powered by the engine or an electric motor. The power assist reduces the effort required to turn the wheels, making steering easier, especially at low speeds or when the vehicle is stationary.
Advantages and disadvantages
Both manual and power steering gear boxes have their pros and cons:
Manual Steering Gear Box:
- Advantages:
- Simpler design with fewer components
- Lower maintenance requirements
- Better road feel and feedback
- Lighter overall vehicle weight
- Disadvantages:
- Requires more physical effort, especially at low speeds
- Can be tiring during long drives or in heavy traffic
- May be challenging for some drivers, particularly those with limited upper body strength
Power Steering Gear Box:
- Advantages:
- Easier to steer, requiring less physical effort
- Improves maneuverability, especially in tight spaces
- Reduces driver fatigue during long trips
- Enhances safety by allowing quicker steering response
- Disadvantages:
- More complex system with additional components
- Higher maintenance requirements and potential repair costs
- Reduced road feel, which some driving enthusiasts may dislike
- Slight increase in fuel consumption due to power draw
Suitability for different vehicles
The choice between manual and power steering gear boxes often depends on the vehicle type and its intended use:
- Small, lightweight cars: Manual steering can be suitable, providing good feedback and a pure driving experience.
- Sports cars: Some enthusiasts prefer manual steering for better road feel, but many modern sports cars use advanced power steering systems.
- Larger sedans and SUVs: Power steering is almost essential due to the vehicle’s weight and size.
- Commercial vehicles and trucks: Power steering is crucial for safe and comfortable operation.
- Off-road vehicles: Power steering is beneficial for navigating rough terrain and obstacles.
Ultimately, the trend in modern vehicles is towards power steering, with advancements in electric power steering (EPS) systems offering a good balance between ease of use and driving feel. However, some classic car enthusiasts and purists still appreciate the direct connection and feedback provided by manual steering gear boxes.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Common Steering Gear Box Problems

A. Wear and tear signs
As your vehicle ages, the steering gear box naturally experiences wear and tear. Recognizing these signs early can prevent more serious issues down the road. Common indicators include:
- Difficulty turning the steering wheel
- Uneven tire wear
- Steering wheel not returning to center
- Increased play in the steering
It’s crucial to address these symptoms promptly to maintain safe driving conditions and prevent further damage to your vehicle’s steering system.
B. Fluid leaks
Fluid leaks are a telltale sign of steering gear box problems. Power steering systems rely on hydraulic fluid to function properly. When you notice:
- Red or pink fluid puddles under your car
- Low power steering fluid levels
- Whining noise when turning the wheel
These are clear indicators of a potential leak in your steering gear box. Ignoring these signs can lead to complete steering failure and costly repairs.
| Leak Color | Possible Source | Severity |
|---|---|---|
| Red/Pink | Power steering | High |
| Brown | Engine oil | Medium |
| Green | Coolant | High |
| Clear | Water/AC | Low |
C. Steering wheel play
Excessive play in the steering wheel is not only annoying but also dangerous. It can manifest as:
- A loose or wobbly steering wheel
- Delayed response when turning
- Need for constant corrections while driving straight
These issues often stem from worn-out components within the steering gear box, such as bearings or gears. Addressing steering wheel play promptly is crucial for maintaining control of your vehicle and ensuring safety on the road.
D. Noise and vibration issues
Unusual noises or vibrations while steering can indicate problems with your steering gear box. Be alert for:
- Grinding sounds when turning
- Clunking noises during low-speed maneuvers
- Vibrations felt through the steering wheel
- Squealing noises, especially in cold weather
These symptoms often point to issues like worn-out bearings, loose components, or low fluid levels in the steering gear box. Ignoring these warning signs can lead to more severe damage and potentially dangerous driving conditions.
Now that we’ve covered the common steering gear box problems, it’s essential to understand how to maintain your steering system to prevent these issues from occurring or worsening. Regular maintenance can significantly extend the life of your steering gear box and ensure smooth, safe driving experiences.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity

Regular inspections
Regular inspections are crucial for maintaining the longevity of your steering gear box. By conducting routine checks, you can catch potential issues early and prevent more severe problems down the road. Here’s a list of key areas to focus on during your inspections:
- Check for leaks
- Examine the steering linkage
- Inspect the steering shaft
- Look for signs of wear on the steering gear box housing
- Test for unusual noises or vibrations
Performing these checks at least every 6 months or 6,000 miles (whichever comes first) can significantly extend the life of your steering gear box.
Fluid checks and replacement
Proper fluid maintenance is essential for the smooth operation of your steering gear box. Here’s a table outlining the recommended fluid check and replacement intervals:
| Action | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Visual fluid check | Monthly |
| Fluid level check | Every 3 months or 3,000 miles |
| Fluid replacement | Every 2 years or 24,000 miles |
When checking the fluid, look for signs of contamination or discoloration. If the fluid appears dark or has a burnt smell, it’s time for a replacement. Always use the manufacturer-recommended fluid type to ensure optimal performance.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
Lubrication practices
Proper lubrication is key to reducing friction and wear within the steering gear box. Follow these lubrication practices:
- Use high-quality grease specifically designed for steering components
- Apply grease to all fittings and joints connected to the steering gear box
- Lubricate the steering shaft and universal joints
- Pay special attention to the ball joints and tie rod ends
Implement a regular lubrication schedule, typically every 12 months or 12,000 miles, to keep all moving parts functioning smoothly.
Alignment considerations
Proper wheel alignment is crucial for the overall health of your steering system, including the gear box. Misalignment can cause uneven wear on steering components and increase stress on the gear box. Consider these alignment-related tips:
- Have your wheel alignment checked annually or after hitting major potholes
- Pay attention to uneven tire wear, as it’s a sign of misalignment
- Address alignment issues promptly to prevent unnecessary strain on the steering gear box
- Ensure proper tire pressure, as it affects alignment and steering performance
By maintaining proper alignment, you not only extend the life of your steering gear box but also improve overall vehicle handling and tire longevity.
Regular maintenance practices, including inspections, fluid checks, lubrication, and alignment considerations, play a vital role in preserving the functionality and extending the lifespan of your steering gear box. By following these guidelines, you can ensure smooth and reliable steering performance for years to come. In the next section, we’ll explore options for upgrading your steering gear box to enhance your vehicle’s performance and handling capabilities.
Upgrading Your Steering Gear Box
Performance enhancements
Upgrading your steering gear box can significantly improve your vehicle’s handling and overall driving experience. Performance enhancements focus on increasing precision, responsiveness, and durability. Here are some key improvements you can consider:
- Quick-ratio steering boxes
- Heavy-duty components
- Enhanced fluid systems
- Improved seals and bearings
Quick-ratio steering boxes reduce the number of turns lock-to-lock, providing faster steering response. This is particularly beneficial for performance driving and off-road applications. Heavy-duty components, such as stronger gears and shafts, can withstand higher loads and provide better longevity under demanding conditions.
Enhanced fluid systems, including high-performance steering fluids and improved cooling, can reduce wear and maintain consistent performance. Upgraded seals and bearings reduce friction, improve smoothness, and extend the life of your steering gear box.
| Enhancement | Benefits | Ideal for |
|---|---|---|
| Quick-ratio | Faster response, improved handling | Performance driving, racing |
| Heavy-duty components | Increased durability, higher load capacity | Off-road, towing |
| Enhanced fluid systems | Better heat dissipation, reduced wear | High-performance applications |
| Improved seals and bearings | Smoother operation, extended lifespan | All applications |
Retrofit options
For older vehicles or those looking to modernize their steering system, retrofit options provide an excellent solution. These upgrades allow you to install more advanced steering gear boxes in place of older, less efficient units. Popular retrofit options include:
- Hydraulic to electric power steering conversion
- Manual to power steering upgrade
- Recirculating ball to rack and pinion conversion
Each of these retrofits offers unique advantages. For instance, converting from hydraulic to electric power steering eliminates the need for a power steering pump, reducing parasitic power loss and improving fuel efficiency. Upgrading from manual to power steering greatly enhances comfort and control, especially at low speeds or during parking maneuvers.
Compatibility considerations
When upgrading your steering gear box, it’s crucial to ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s existing systems. Consider the following factors:
- Mounting points and physical dimensions
- Steering column interface
- Power steering pump compatibility (if applicable)
- Electrical system requirements (for electric power steering)
- Brake booster clearance
Always consult with a professional or thoroughly research your specific vehicle model before proceeding with an upgrade. Some upgrades may require additional modifications to surrounding components, such as the steering column, tie rods, or suspension geometry.
It’s also important to consider the impact on your vehicle’s handling characteristics. While upgrades generally improve performance, they can also alter the feel of your steering. Test drive the vehicle after installation to ensure you’re comfortable with the new steering dynamics.
10 FAQs
Q1: What is a steering gear box?
A steering gear box is a crucial component of a vehicle’s steering system that converts the rotational motion of the steering wheel into linear motion, which then moves the wheels. It’s responsible for translating the driver’s input into precise directional control of the vehicle.
Q2: How often should I have my steering gear box inspected?
Regular inspections are essential for maintaining your steering gear box. As a general rule:
- For normal driving conditions: Every 50,000 miles or annually
- For severe driving conditions: Every 30,000 miles or semi-annually
| Driving Condition | Inspection Frequency |
|---|---|
| Normal | 50,000 miles / Annually |
| Severe | 30,000 miles / Semi-annually |
Q3: What are signs of a failing steering gear box?
Common indicators include:
- Steering wheel play or looseness
- Difficulty turning the wheel
- Unusual noises when steering
- Fluid leaks under the vehicle
- Uneven tire wear
Q4: Can I replace a steering gear box myself?
While it’s possible for experienced DIY mechanics, replacing a steering gear box is a complex task that often requires specialized tools and knowledge. It’s generally recommended to have this job done by a professional mechanic to ensure proper installation and alignment.
Q5: How long does a steering gear box typically last?
The lifespan of a steering gear box can vary depending on several factors:
- Vehicle make and model
- Driving conditions
- Maintenance habits
On average, a well-maintained steering gear box can last between 100,000 to 200,000 miles.
Q6: What’s the difference between a rack and pinion and a steering gear box?
While both systems serve the same purpose, they differ in design and operation:
| Steering Gear Box | Rack and Pinion |
|---|---|
| Uses a worm gear | Uses a pinion gear on a toothed rack |
| Common in older vehicles and trucks | More common in modern passenger cars |
| Generally more durable | Typically more responsive |
Q7: How does power steering affect the gear box?
Power steering reduces the effort required to turn the steering wheel by using hydraulic or electric assistance. This puts less stress on the steering gear box, potentially extending its lifespan and improving overall steering performance.
Q8: What type of fluid is used in a power steering gear box?
Most power steering systems use specific power steering fluid, but some may use automatic transmission fluid (ATF). Always consult your vehicle’s manual for the correct fluid type.
Q9: Can a steering gear box be rebuilt?
Yes, in many cases, a steering gear box can be rebuilt rather than replaced. This process involves disassembling the unit, replacing worn parts, and reassembling it. Rebuilding can be a cost-effective alternative to full replacement, especially for older or rare vehicles.
Q10: How does a steering gear box affect vehicle alignment?
The steering gear box plays a crucial role in maintaining proper wheel alignment. A worn or misadjusted gear box can lead to alignment issues, resulting in uneven tire wear, poor handling, and decreased fuel efficiency. Regular inspections and maintenance of the steering gear box are essential for maintaining proper alignment and overall vehicle performance.
The steering gear box is a critical component of your vehicle’s steering system, responsible for translating the rotational motion of the steering wheel into the linear motion that turns your wheels. Whether you have a manual or power steering gear box, understanding its function and maintenance is crucial for safe driving and prolonged vehicle life.
Regular maintenance, such as checking fluid levels and addressing unusual noises or steering difficulties promptly, can significantly extend the lifespan of your steering gear box. For those looking to enhance their vehicle’s performance, upgrading to a more advanced steering gear box can offer improved handling and responsiveness. Remember, a well-maintained steering system not only ensures a smoother ride but also contributes to your safety on the road.
Visit website: Autobiography Zone
